Dynamics 365 Tutorials, Supply Chain and Logistics Management
Maximize Throughput and Accuracy of Your Warehouse Operations with Cluster Picking in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain

Transform Warehouse Operations with Cluster Picking in D365
Case Quantities | Work Order | Work Order Templates | Feature Management | Cluster Picking
What is Warehouse Order Picking?
Warehouse order picking procedures are critical in every warehouse. Compared to shipping, storage and receiving, order picking may account for up to 55% of a distribution center’s running expenditures. Additionally, it has a direct effect on your consumers’ level of satisfaction. Therefore, your firm will prosper if your warehouse picking processes are rapid and precise. Let’s look at how to execute essential warehouse picking best practices.
Learn more about our courses that provide you with the fundamental skills need to achieve six-figure employment opportunities in the sector.
SUMMARY
Warehouse order picking may account for up to 55% of a distribution center’s running expenditures. As a result, order picking has a direct effect on your consumers’ level of satisfaction. What you need to know about order picking and how to execute essential warehouse picking best practices are included in this blog.
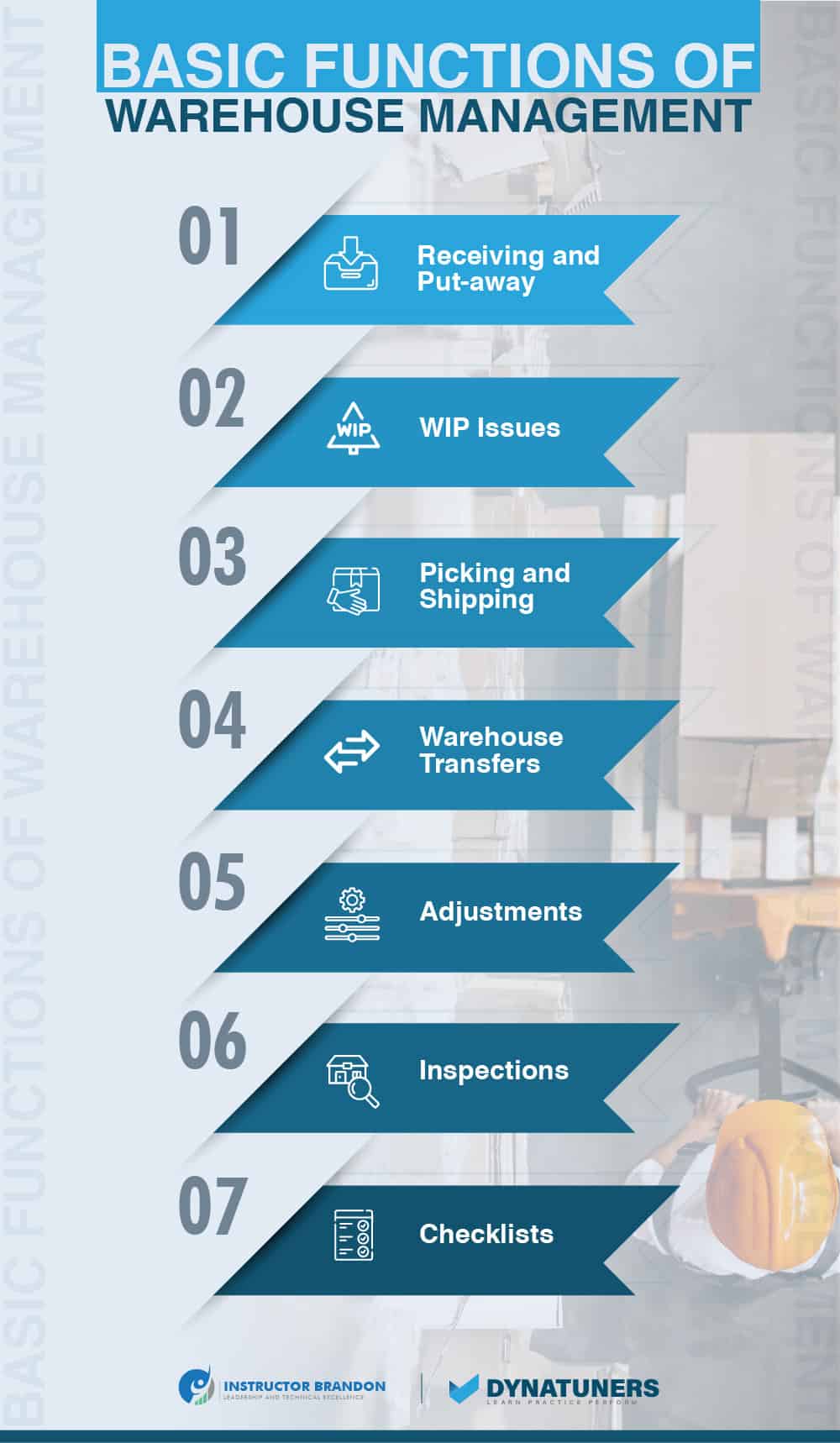
Management of Warehouses
The automation of warehouse management offers clients more freedom and choice. It further allows warehouse procedures to enable cost savings, which may be passed on to consumers in cheaper pricing.
While agile procedures provide clients with choice and flexibility in terms of delivery, it also:
- Enhances efficacy via the use of sophisticated picking tactics, such as cluster picking.
- Uses innovative put-away procedures, efficiently store incoming products.
- Increases flexibility by establishing processes for put-away and pickup actions without coding. Determine the unique workflow by using filter capabilities.
- Issues material handling instructions to warehouse employees as per the system’s specifications or the user’s instructions (task interleaving).
- Waves of processing: automated, manual, batch-time scheduling, filtering and grouping, and container calculations and packing.
- Enhances tracking and tracing of items via serial number registration throughout the picking process and batch number support with expiry date-based selection techniques.
- Reduces transportation costs by containerizing goods and automating volume and weight estimates.
- Utilizes warehouse workflow to manage sales order returns.
SUMMARY
The automation of warehouse management offers clients more freedom and choice in terms of delivery. It also allows warehouse procedures to enable cost savings, which may be passed on to consumers in cheaper pricing. Automated warehouse processes include batch-time scheduling, filtering and grouping, and container calculations and packing.
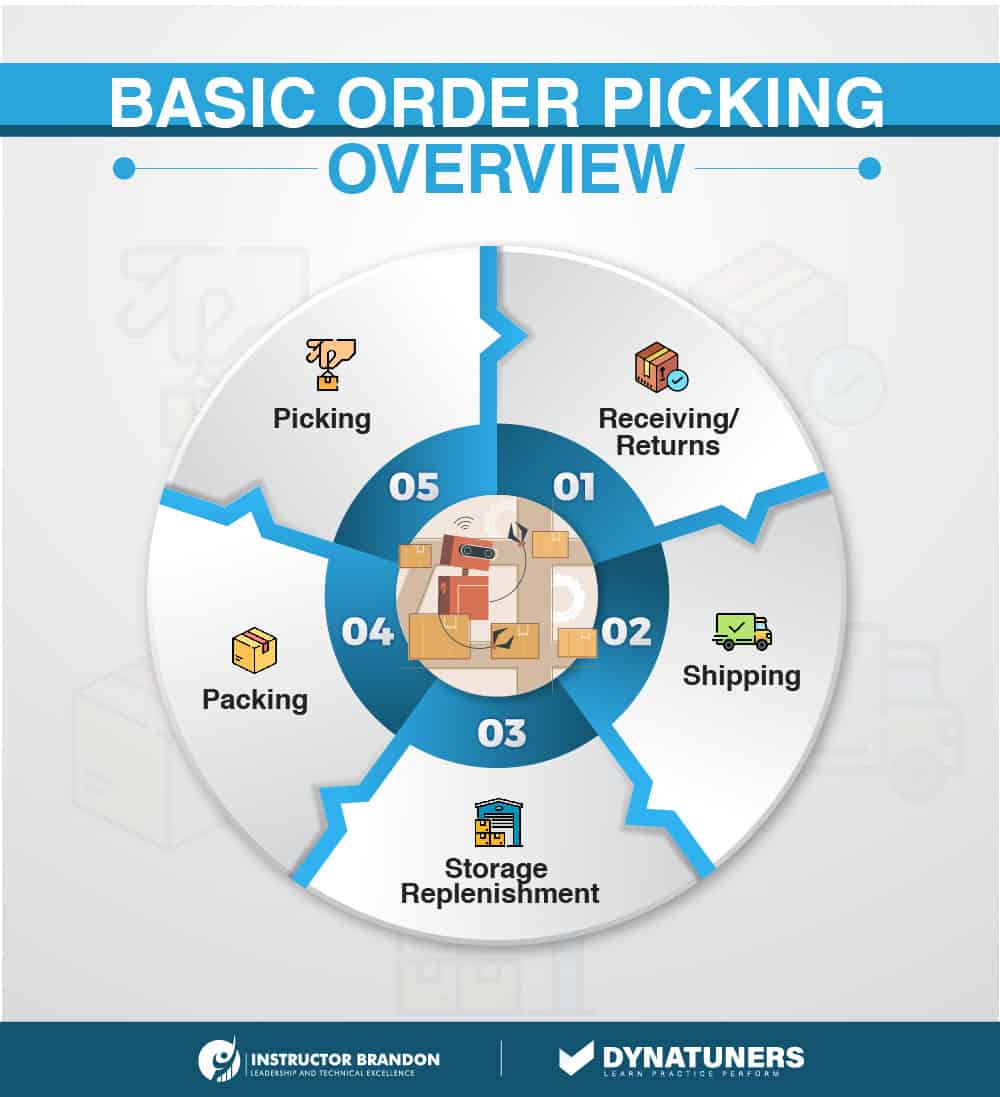
What is Order Picking?
Order picking is the process of selecting products from a warehouse inventory to fulfill several separate client orders. This is a critical step in the supply chain process and has traditionally been regarded as the most labor-intensive and costly operation in any warehouse. As previously stated, order picking costs are anticipated to account for up to 55% of total warehouse operating expenditures. Due to the high cost of order picking and its direct impact on customer satisfaction, businesses are focusing their efforts on streamlining their procedures to establish a more effective supply chain. Get in touch with us as Dynatuners offers a cutting-edge help desk solution for resolving all of your Microsoft Stack technical issues.
SUMMARY
Order picking is regarded as the most labor-intensive and costly operation in any warehouse. Order picking costs are anticipated to account for up to 55% of total warehouse operating expenditures. As a result, businesses are focusing efforts on streamlining their procedures to establish a more effective supply chain.
Types of Order Picking Methods in the Warehouse
There are several picking methods in a warehouse, and each one provides a unique answer for each organization. Depending on the size of your warehouse and inventory, the number of staff available, and the volume of daily client orders, some ways might prove to be more efficient for you as compared to others. Consider the following order selecting scenarios in the warehouse and see how you may get excellent guidance and effective supply chain management so you can concentrate on building your company.
-
Picking Individual Orders
Single order picking is the most prevalent sort of picking. The picker is given one order at a time and then travels to the warehouse to locate each item on order before finishing it. However, the order in which orders are handed to pickers and the paths they take are often not optimum. To fulfill a single order, the worker must constantly make a complete circuit of the warehouse. This is a less-than-optimal approach. WMSs can assist in resolving this issue and increasing productivity.
In this situation, employees may manually or automatically choose many orders simultaneously. The manual picking environment works by enabling the picker to select various SKUs necessary for different orders simultaneously. This reduces travel time. The worker stays in one spot during automated picking, while horizontal and vertical carousels deliver the appropriate SKUs to the worker.
-
Multi-Batch Order Picking
This is the optimal pick and pack option for situations requiring the distribution of many smaller orders. These instructions are more effective for employees who travel significant distances inside a warehouse. Multi-batch picking gathers orders from many locations across the warehouse, reducing order pick times by collecting multiple orders concurrently. Additionally, this approach minimizes the time required to handle several SKUs.
This strategy splits the warehouse into zones and assigns staff to operate only inside those zones. Each zone may use its technology and storage system based on the SKUs stored in that zone and the storage technology employed in that zone. Orders may be picked up from zone to zone in the past or delivered to a designated location before delivery.
This method entails passing orders for fulfillment from one zone to another. For example, if an order originates in zone A, a worker completes the order by adding all needed SKUs from that zone before it is sent to zone B. This process is continued until all products are ready for shipment. Order management software (OMS) may be used to control the order flow in this approach to enhance productivity.
-
Order Consolidation
This is a process that may be used instead of picking and packing. Each zone concurrently determines the SKUs necessary for the order. When a partial order for one zone is completed, it is sent to consolidation until the SKUs for the other zones arrive. When all SKUs are in one location, the partial orders are combined into a single big order. This order is subsequently sent to the shipping department. This is a very sophisticated technique that necessitated the use of inventory management software (IMS).
In this system, totes containing individual orders are transported between zones and delivered to picking stations where workers choose from carousels. These batch stations have specialized technology to ensure that the right amount of material is provided to each tote. The bulk components of orders may be selected throughout this procedure by forklifts employees who pick one order at a time or batch picking. Consolidation brings all of these components together.
Discover case studies of our successfully implemented solutions for a variety of business performance concerns for leading corporations worldwide.
|
Sr. |
Order Management KPIs | |||
| KPI | Overview | Best Practices | Calculation | |
| 1. | Order Shipment Cycle Time | The number of hours required to process a customer order, from the time when the order is placed until the time the order is shipped by the supplier. | · Up-to-date inventory management systems and demand forecasting. · Well defined inventory location procedures to minimize order picking time. .Standardize formats of purchase orders to minimize need for order verification. |
Sum of Time to Ship Customer Orders / Total Number of Customer Orders Shipped |
| 2. | Perfect Customer Order Rate | A composite score calculated by multiplying average on-time delivery rate, complete shipment rate, undamaged shipment rate and correct documentation rate for a certain period of time or group of shipments, as a percentage. | · Accurate demand forecasting and minimal backorder rates.
· Well defined materials management and freight handling procedures to minimize damage. · Frequently review customer database to ensure records are up-to-date. |
On-Time Customer Order Delivery Rate * Complete Customer Order Rate * Undamaged Customer Order Rate * Percentage of Customer Orders with Correct Documentation |
| 3. | On-time Shipment Readiness | The total number of orders picked, packed and ready for shipment by the designated shipping time divided by the total number of orders shipped over the same period of time, as a percentage. | · Staff warehouse appropriately to correspond with increases in order demand.
· Perform routine preventative maintenance on order picking equipment to reduce downtime. · Regularly audit order processing and entry methods to assess areas of improvement. |
(Total Number of Orders Shipped by the Designated Time / Total Number of Orders Shipped) * 100 |
| 4. | On-time Customer Order Delivery Rate | The total number of shipments received by customers on or before the committed shipping time or delivery date divided by the total number of shipments made over the same period of time, as a percentage. | · Accurate demand forecasting and minimal backorder rates.
· Well-maintained distribution and warehousing equipment to minimize delays. · Speedy order entry and order processing methods. |
Number of Shipments Received by Customers On Time / Total Number of Shipments Made) * 100 |
| 5. | Proof of Delivery Rate | The number of shipments that were completed with a signed proof of delivery (POD) form (paper or electronic) divided by the total number of deliveries completed over the same period of time, as a percentage. | · Provide incentives for high rates of Proof of Delivery.
· Use electronic Proof of Delivery systems to track where and when shipments are made. · Adequate training programs to emphasize the importance of Proof of Delivery documents. |
(Number of Shipments Signed / Total Number of Shipments Completed) *100 |
SUMMARY
There are several ways to pick individual orders in a warehouse. WMSs can assist in resolving this issue and increasing productivity. Multi-batch picking is used to gather orders from many locations across the warehouse. This strategy splits the warehouse into zones and assigns staff to operate inside those zones. Pick and Pass involve passing orders for fulfillment from one zone to another.
Order management software may be used to control the order flow in this approach. In addition, advanced Systems Picking involves specialized technology to ensure that the right amount of material is delivered to each tote.
What is Cluster Picking?
Cluster picking is the technique through which an order picker fulfills numerous orders concurrently without intermixing them. Cluster picking may be accomplished by picking straight into a tote equipped with slots to keep the orders separate or directly into a shipping container fitted with a locking mechanism that keeps the containers together. Pick accuracy and efficiency may be increased by using cart picking and pick-to-light technologies.
An obvious benefit of this method is that SKUs and orders are fulfilled in bulk. Additionally, this strategy enables the picker to finish orders by placing products straight into their shipping containers, eliminating the need to sort the gathered SKUs afterward. Cluster picking is often used in conjunction with piece-picking and other types of picking procedures.
This is owing to cluster picking’s adaptability and the fact that its operations do not need the substitution of different techniques. This will vary according to the order profiles you manage and the velocity of the SKUs in your warehouse. Generally, this strategy is best suited for a large number of SKUs with a slower pace. Its implementation would be insufficient for high-volume orders requiring high-volume SKUs since the procedure is still mostly manual. Read our latest blog on pricing approaches to learn more on Dynamics 365 functionalities.

SUMMARY
Cluster picking is the technique through which an order picker fulfills numerous orders concurrently without intermixing them. Pick accuracy and efficiency may be increased by using cart picking and pick-to-light technologies. Cluster picking is often used in conjunction with piece-picking and other types of picking procedures.
Cluster Picking in Dynamics 365
Picking individual minor parts or component orders is sometimes inconvenient and labor-consuming. These inefficiencies are exacerbated when the picking process requires a wide warehouse footprint, requiring your personnel to spend more commuting than handling orders.
Cluster picking, which utilizes a mobile device, is an efficient pick technique that enables you to select numerous orders in a single run through the warehouse. It is a selection option in Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Supply Chain.
Cluster selection in D365 SMC is configurable in the following ways:
-
Cluster Profiles
Customer profiles define whether to produce cluster IDs automatically, the number of locations to utilize when to break clusters, and how to sequence and check picking activities.
Work templates describe how cluster picking tasks are created.
-
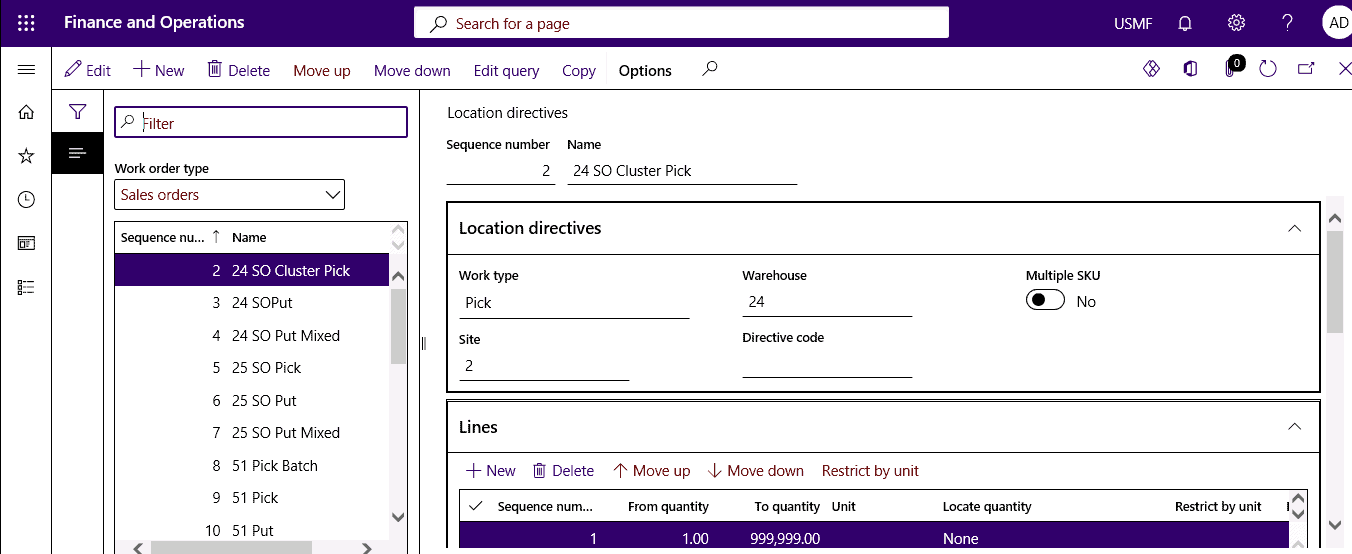
Location Directives
Location directives describe the location of things to be picked up and stored.
-
Parameters for Warehouse Management
Parameters for warehouse management indicate the number sequence to utilize while generating cluster IDs.
SUMMARY
Picking individual minor parts or component orders is sometimes inconvenient and labor-consuming. Cluster picking, which utilizes a mobile device, is an efficient picking technique. It enables you to select numerous orders in a single run through the warehouse.
Functional Walkthrough of Cluster Picking in Microsoft Dynamics 365
Prerequisites for enabling cluster picking:
Step 1
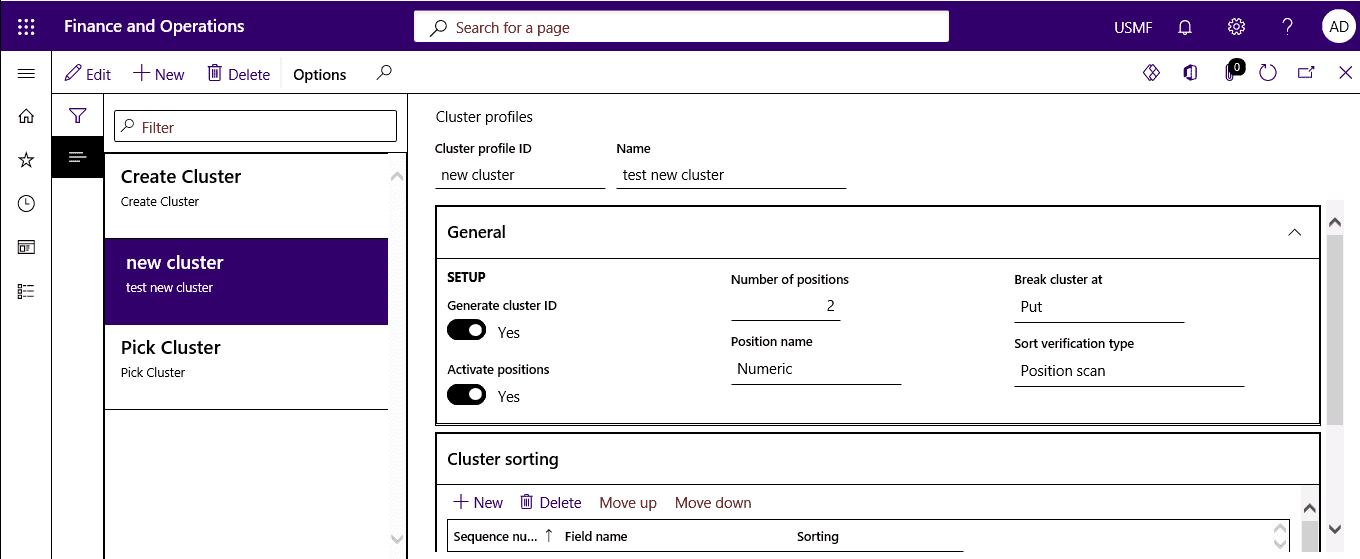
Click Warehouse management > Setup > Mobile device > Cluster profiles.
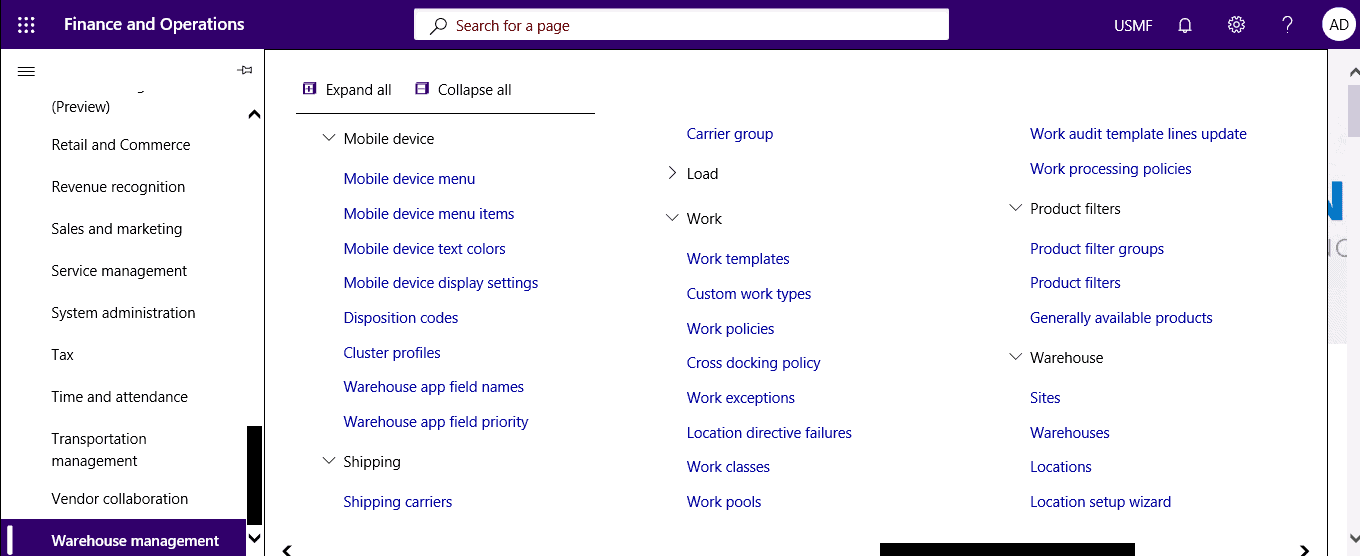
Step 2
Specify whether to generate cluster IDs automatically, the number of positions, break clusters, etc.
Work Templates
Step 1
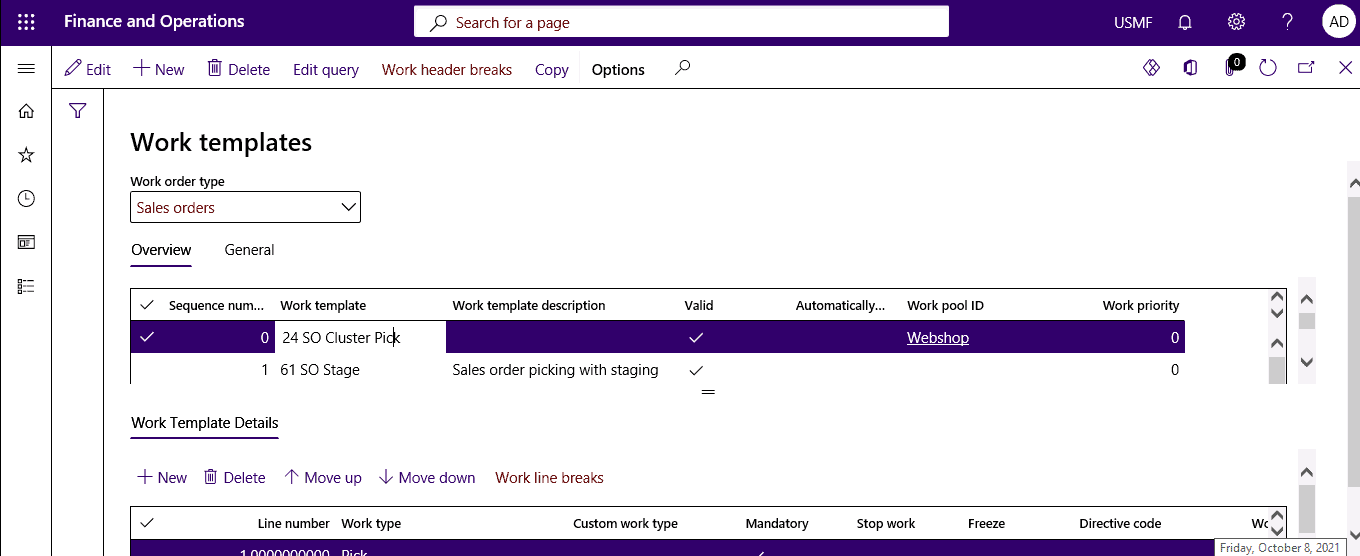
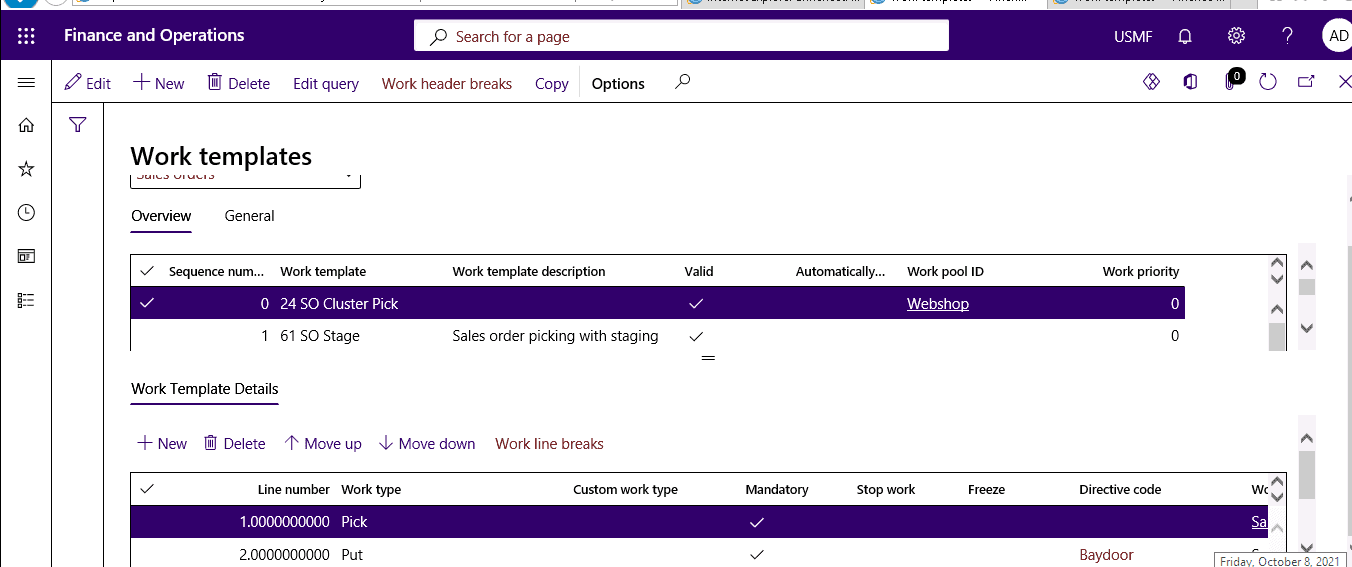
Click Warehouse management > Work > Work templates.
Step 2
Define how to create the picking work for cluster picking.
Location Directives
Step 1
Select Warehouse management > Setup > Location directives.
Step 2
Specify where to pick items from and where to put them.
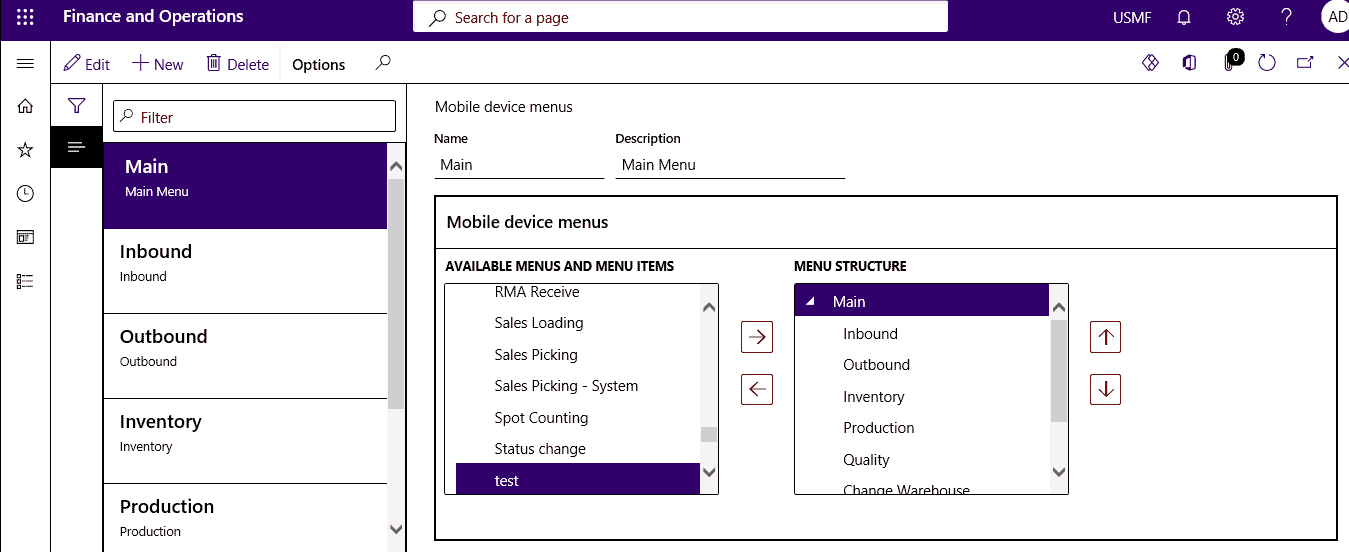
Mobile Device Menu Items
Step 1
Click Warehouse management > Setup > Mobile device > Mobile device menu items.
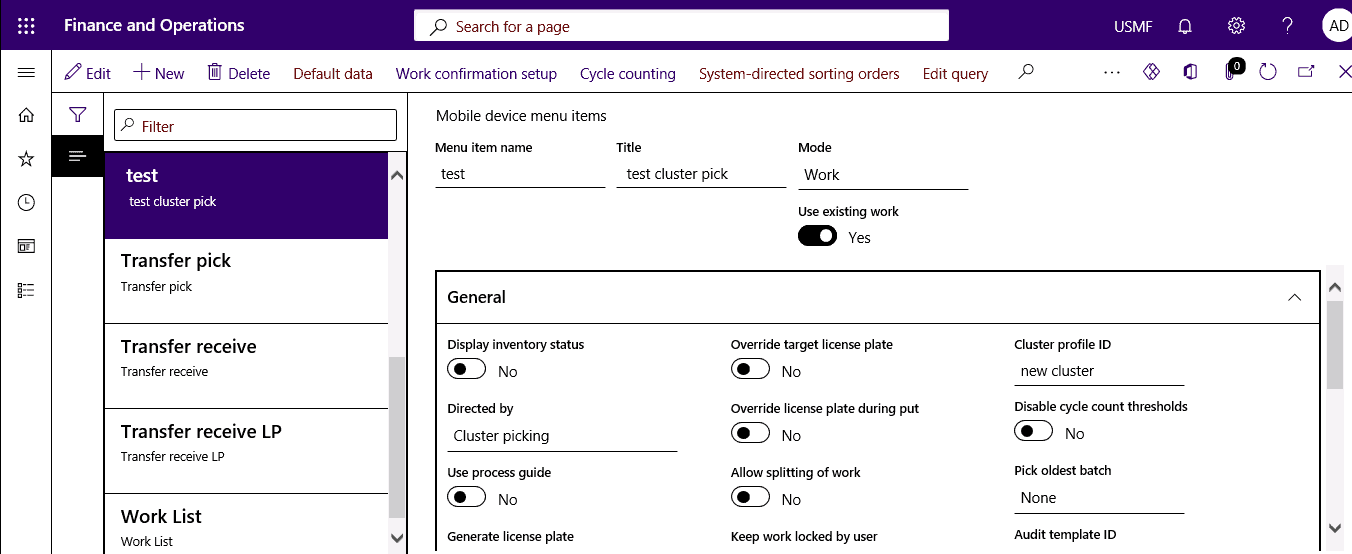
Step 2
Configure a mobile device menu item to use existing work that is directed by cluster picking.
Step 3
Click Warehouse management > Setup > Mobile device > Mobile device menu.
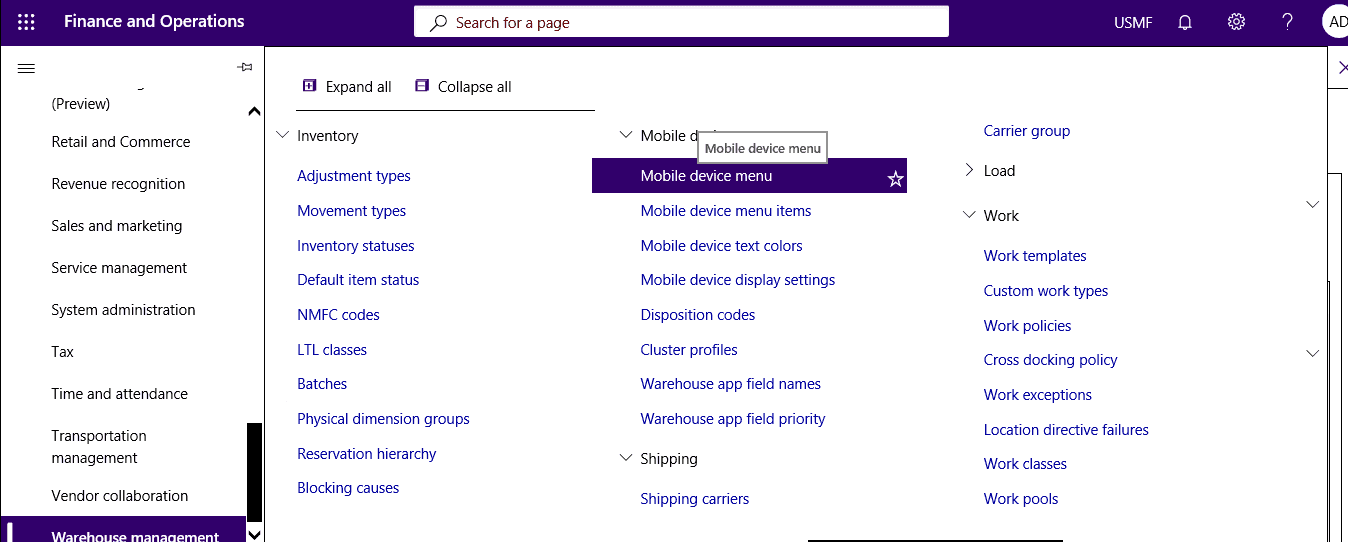
Step 4
Add the menu item to a mobile device menu so that it is displayed on mobile devices.
Warehouse Management Parameters
Step 1
Select Warehouse management > Setup > Warehouse management parameters.
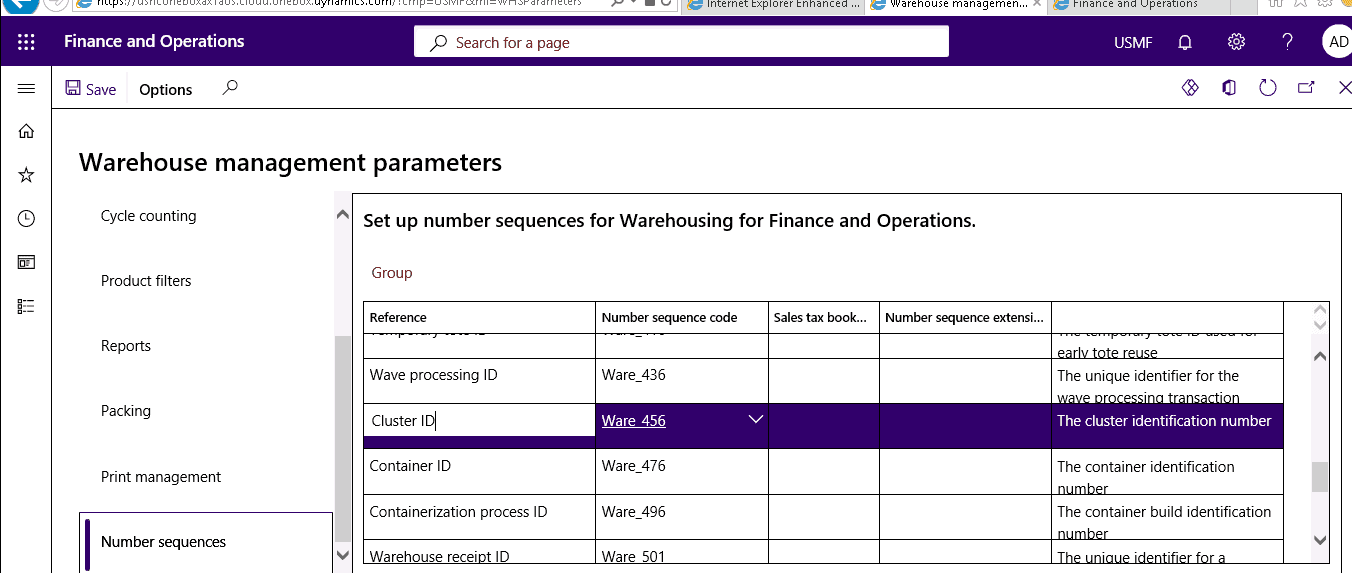
Step 2
Specify the number sequence to use if you want to generate identifiers for clusters.
Set up a Cluster Profile
Step 1
Click Warehouse management > Setup > Mobile device > Cluster profiles.
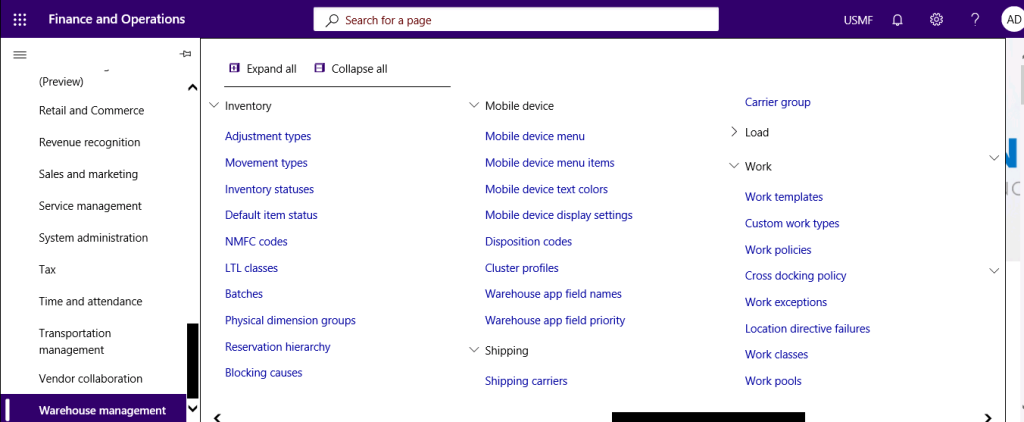
Step 2
Click New to create a new profile.
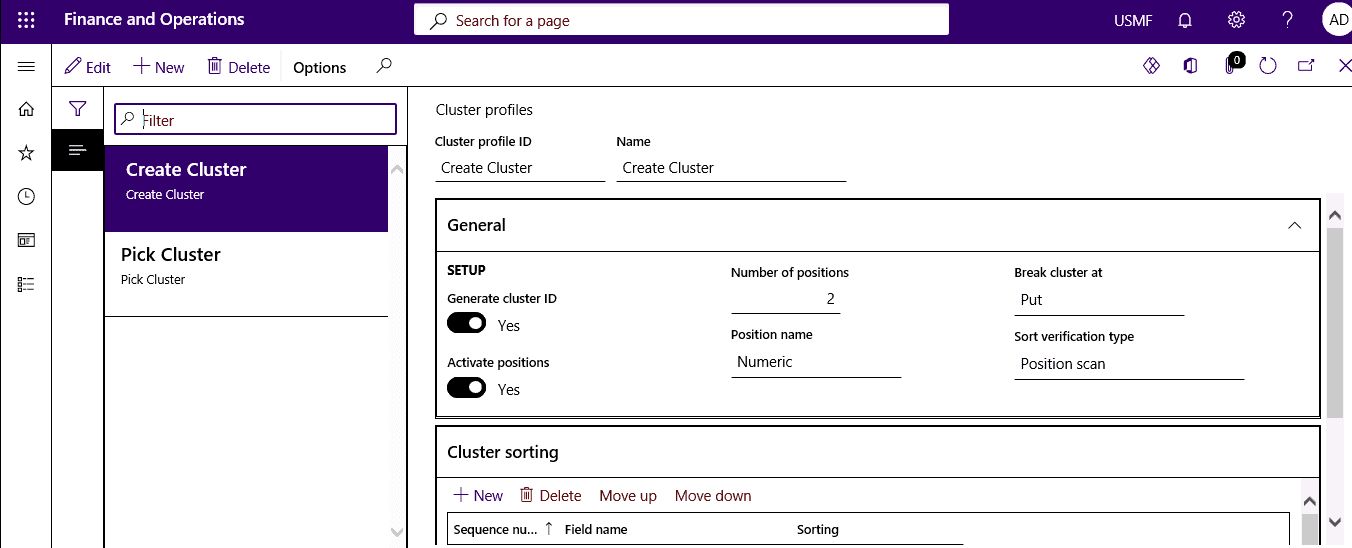
Step 3
In General, specify whether to automatically generate cluster IDs, the number of positions to use, when to break clusters. Then, in Cluster sorting, click New to set up the sorting criteria for the cluster.
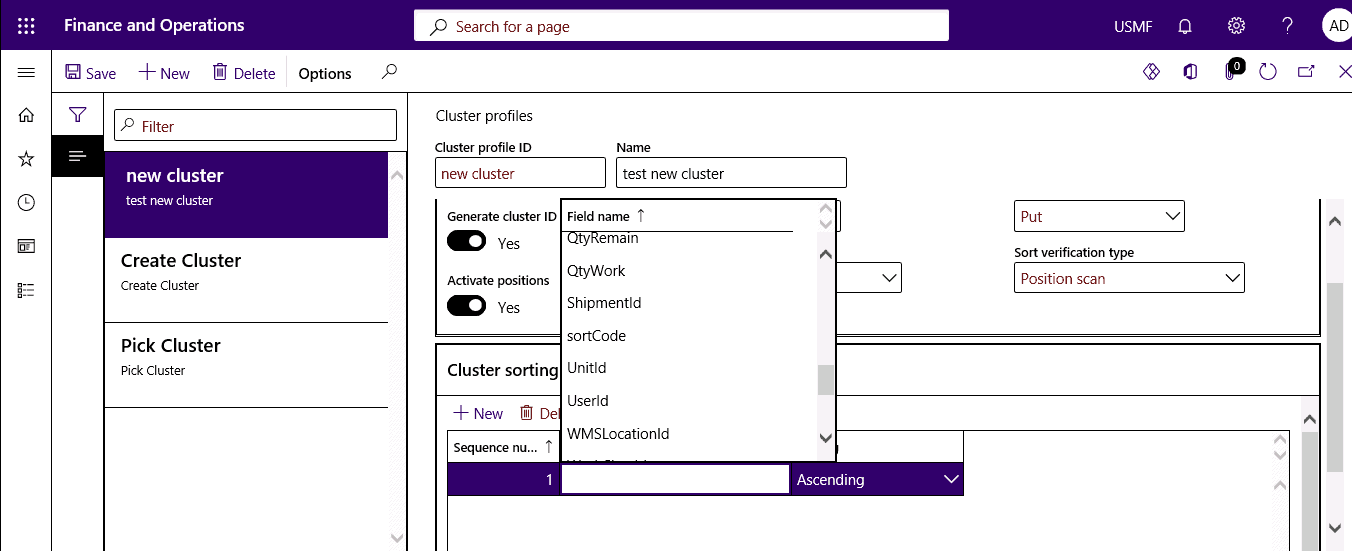
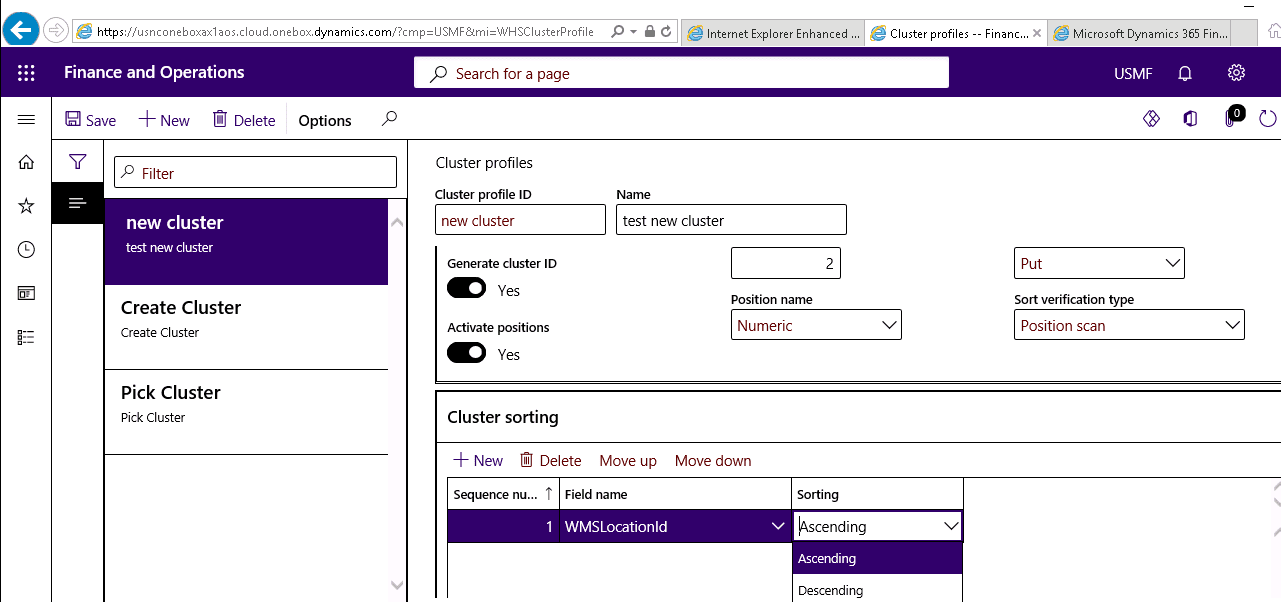
Step 4
In the Sequence number field, enter a number to define the order in which the sorting criteria are processed. In the Field name, select the field that will determine the sorting. In the Sorting field, select ascending or descending.
Set Up Item Verification with Cluster Picking
Step 1
Select Warehouse management > Setup > Mobile device > Mobile device menu items.
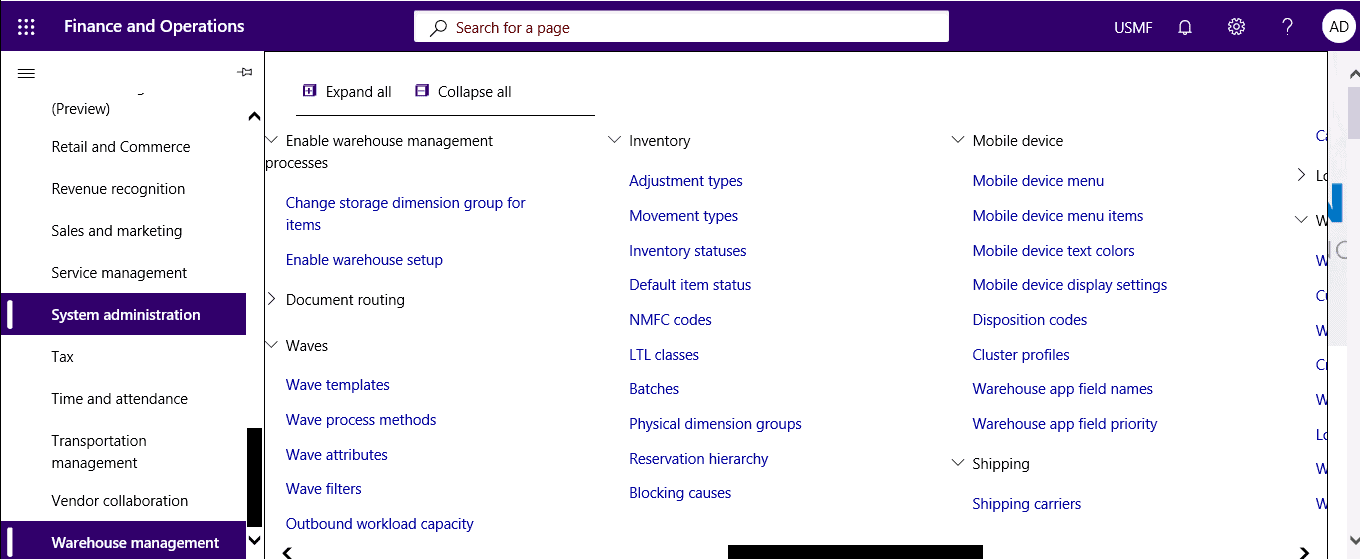
Step 2
From the mobile device menu item, click Work confirmation set up in the action pane.
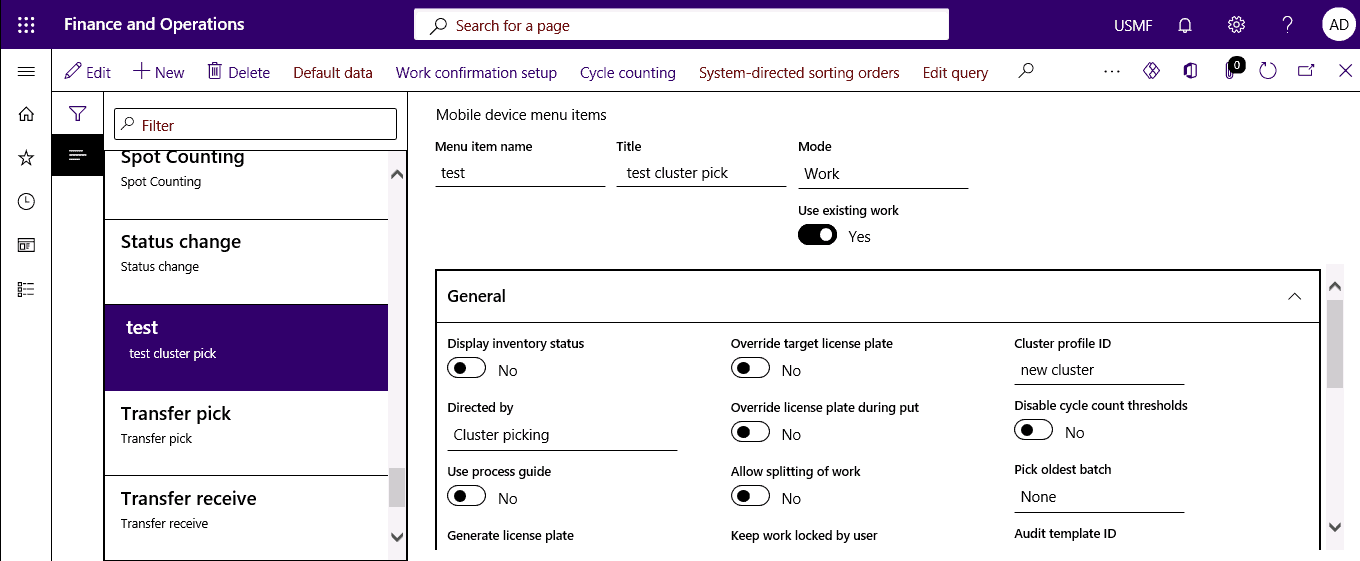
Step 3
The product confirmation option allows you to verify each piece of inventory from the mobile device when scanned.
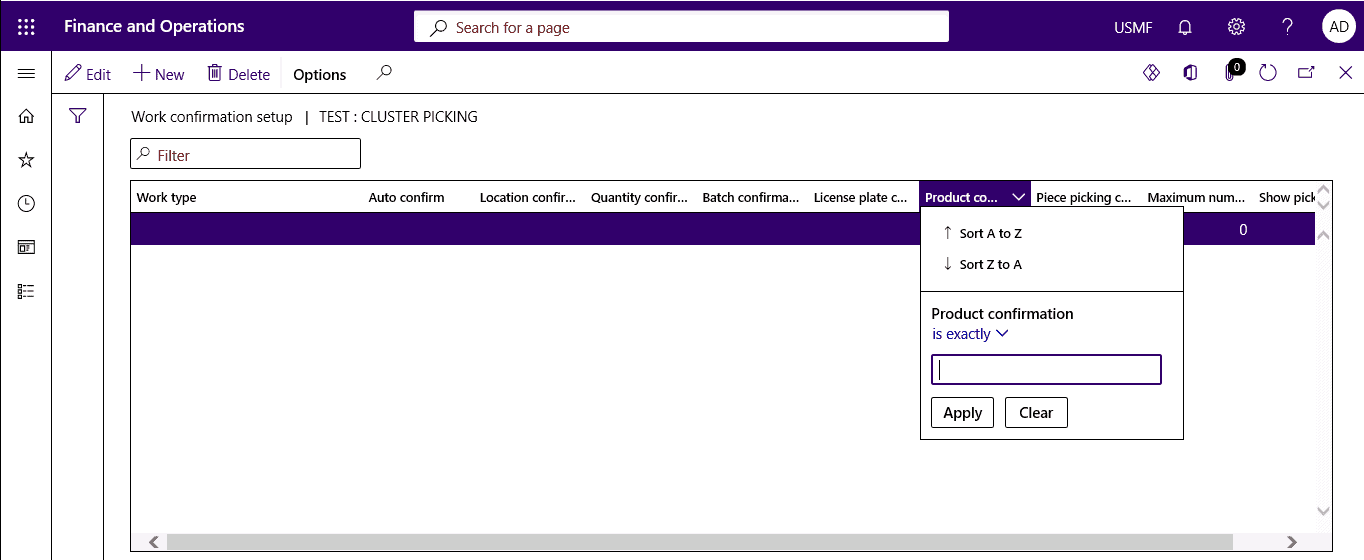
SUMMARY
To enable cluster picking, you must set up Cluster profiles, Work templates, Location directives, Mobile device menu items, and Warehouse management parameters by following the above steps.
Final Thoughts
As operations managers attempt to boost productivity, throughput, and accuracy while also reducing costs, they may wonder, “What is the optimum order picking method?” Unfortunately, there is no one-size-fits-all strategy for order selection since it all relies on your operation’s requirements. Instead, an intelligent way to begin is by asking a few straightforward questions.
- How large is your warehouse?
- How many SKUs do you have in stock?
- How many orders do you handle daily?
- How many lines are typically included in an order?
- How many hours does it take an order picker to complete your daily orders?
These criteria must be examined and considered when determining the optimal way of order selection for your organization. An expert material handling integrator can assist you in analyzing your data and navigating the many technologies available to elevate your picking process.
SUMMARY
There is no one-size-fits-all strategy for order selection since it all relies on your organization’s requirements. However, an expert material handling integrator can assist you in analyzing your data and navigating the many technologies available to elevate your picking process. An intelligent way to begin is by asking a few straightforward questions.
At Instructor Brandon | Dynatuners, we always seek innovative methods to improve your competitiveness and suit your Microsoft Dynamics 365 requirements. Our offerings are founded on defined procedures, industry experience, and product understanding. If you’re interested to consult with our specialists on how to effectively use cluster picking as your picking methodology for your operations, don’t hesitate to Contact Us.
[sc_fs_multi_faq headline-0=”h2″ question-0=”What is D365’s cluster picking feature?” answer-0=”Cluster picking is a method of choosing products for many orders concurrently by grouping them into pick clusters. You will then just need to visit the pick-up location once. Typically, this feature is utilized for choosing small orders or amounts less than a case. ” image-0=”” headline-1=”h2″ question-1=”What exactly is cluster order picking?” answer-1=”Cluster picking is the technique through which an order picker fulfils numerous orders concurrently without intermixing them. Cluster picking may be accomplished by picking straight into a tote equipped with slots to keep the orders separate or directly into a shipping container equipped with a locking mechanism that keeps the containers together. ” image-1=”” headline-2=”h2″ question-2=”What are the distinctions between cluster picking and batch picking? ” answer-2=”Workers choose each order independently during a journey through a DC or zone in discrete order picking. By comparison, batch picking (also known as cluster picking) is a warehouse order picking approach in which employees choose numerous orders during each trip through a distribution center or zone within a distribution center. ” image-2=”” count=”3″ html=”true” css_class=””]
 2550
2550