Dynamics 365 Tutorials, Supply Chain and Logistics Management
How to Set up Maintenance Plans for Assets in Dynamics 365
Setting up Maintenance Plans in Microsoft Dynamics 365
Types of Assets | Supply Chain Processes | Asset Tracking | Maintenance Plans | Inventory Management
Effective maintenance planning is critical to the maintenance environment’s overall sustainability. The components of the maintenance plan, which comprise the actual work to be performed, instructions, a timeline, workers, spare parts, and contractors, serve as a guide for all maintenance work tasks.
What is a Maintenance Plan?
A maintenance plan is a document that details the work required to maintain the assets in a facility preventatively. The purpose of maintenance planning is to guarantee that your equipment remains in good working order. While a standard plan may suffice, any facility will require a comprehensive program to get the full benefits of your maintenance policy.
A comprehensive plan should include all aspects of your facility’s maintenance strategy. The program should include a comprehensive inventory of the assets you are responsible for maintaining. The comprehensive list, which covers several elements in manufacturing companies, such as boilers, pumps, and roofs, ensures that no critical asset is overlooked. Additionally, you must specify the exact maintenance tasks that you intend to do. Wherever possible, associate these tasks with specific assets. A realistic maintenance schedule should also be enough to guide the entire program of maintenance. To maintain your assets efficiently, you must demonstrate the skill set required for each maintenance operation. You do not want to hire someone who is insufficiently skilled to perform maintenance. Are you ready for the next step in your career? Check out our latest beginner and certificate-level courses.
SUMMARY
Effective maintenance planning is crucial to ensuring long-term sustainability. A thorough maintenance strategy should include all facets of your facility’s operation. It should include an inventory of the assets for which you are accountable, as well as a timetable and thorough descriptions of each item.
The Critical Nature of a Strategic Maintenance Plan
When it comes to maintenance operations, reliability is the most important characteristic. Businesses rely on equipment to carry out critical business functions. When an equipment fails, unscheduled downtime has a negative effect on overall productivity. By developing and implementing a comprehensive strategy for asset management, you can remove inefficiencies and assure the consistency of essential processes. Utilizing any maintenance method is preferable to taking none at all. Maintenance is far too chaotic, problematic, and disorganized to be productive with a hit-and-miss strategy. As a result, inefficient asset management places the business — and, more significantly, the employees — in grave danger.
As a result, determining how your facility will approach equipment maintenance strategically is one of the most critical business decisions an organization can make. However, no single solution will fit perfectly into your unique asset infrastructure. Rather than that, Michael Guy Deighton’s study indicates that the selection process frequently comprises a combination of maintenance tactics. In simpler terms, combining various methods enables you to determine the most optimal approach for your organization’s particular maintenance activity. If you want to learn more about how to implement asset leasing, read our blogs.
SUMMARY
Businesses depend on equipment to perform mission-critical operations. With a hit-or-miss technique, maintenance is simply too chaotic, troublesome, and unorganized. You may eliminate inefficiencies by establishing and executing a comprehensive, enterprise-wide asset management plan.
What are the Different Types of Maintenance Strategies?
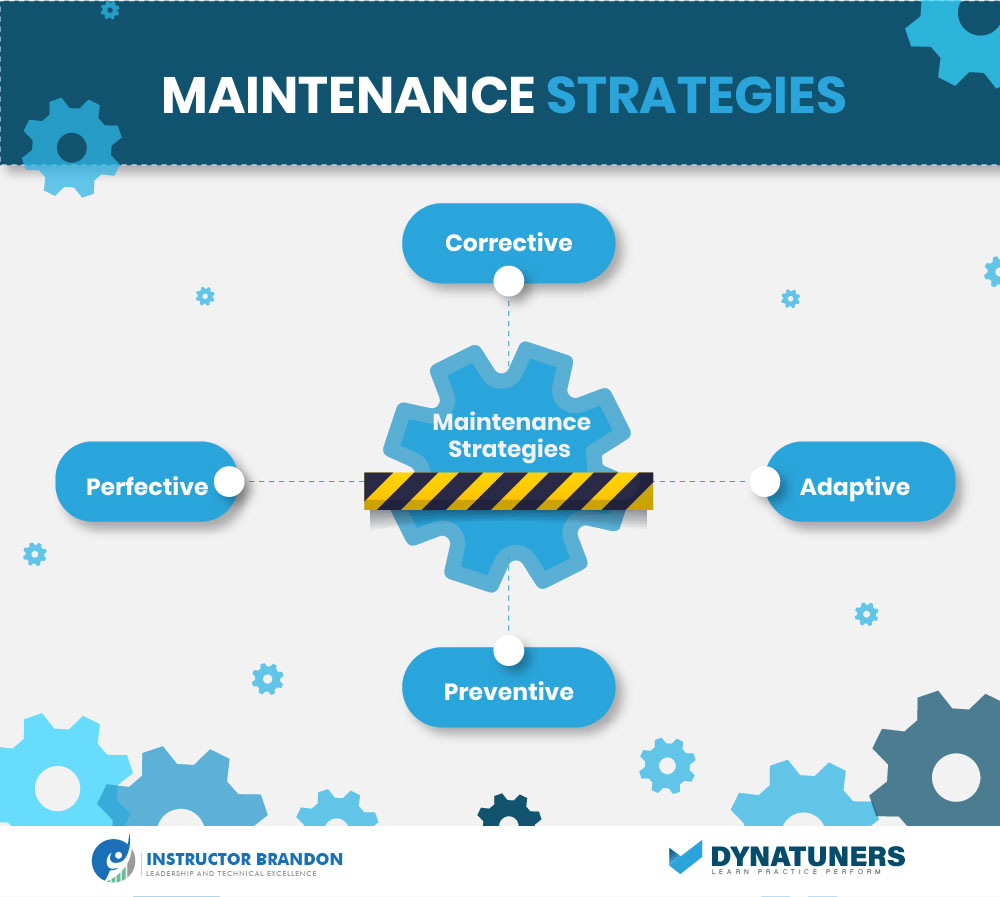
When it comes to an equipment maintenance plan, there are two broad umbrella categories: preventative and corrective maintenance. These two systems are opposed to the whole range of asset management. It is critical to first grasp what each umbrella phrase means. As the name implies, preventive maintenance (PM) is all about preventing asset failure before it occurs. Alternatively referred to as preventative maintenance, this method comprises all maintenance operations aimed to ensure that equipment performs its essential duties as reliably as feasible. Simply said, PM steers clear of disturbances such as equipment failure or unscheduled downtime.
By contrast, corrective maintenance takes a proactive approach to asset management. Rather than strategizing to minimize or prevent asset failure, firms that follow this paradigm prefer to handle disruptions after they occur. Corrective maintenance therefore becomes a competition to minimize downtime (and the accompanying productivity losses). While each technique has its advantages, neither is without drawbacks. Organizations often use a mix of the two. However, you’ll need to be familiar with their subdivisions.
Consider the following particular preventative maintenance strategies:
- Time-based maintenance refers to the practice of maintenance employees doing repairs or restorations at predetermined intervals of time. In essence, they arrange maintenance work ahead of time.
- Maintenance activities are targeted to identify failures in protective assets rather than essential assets in this technique. Because protective equipment is only employed in the event that vital assets fail, it is crucial to ensure that it is functioning properly before it is required. To put it another way, it’s a fail-safe mechanism.
- Condition monitoring enables a facility to determine which equipment needs repair and which is performing well. This technique entails assessing the health of essential assets to identify whether repairs are required in the long or short term.
- As an extension of condition-based maintenance, predictive maintenance forecasts asset failure using smart technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. IoT sensors gather performance data to identify when equipment will break and when maintenance is most cost-effective.
- Using risk-based technique, maintenance jobs are assigned based on risk assessment. Essentially, assets that pose the greatest risk need maintenance on a more regular basis.
SUMMARY
The goal of preventative maintenance (PM) is to avert asset breakdown before it happens. Corrective maintenance strategizes to avoid or limit asset failure. Organizations adhering to this paradigm choose to deal with disruptions as they arise. Additionally, some preventive maintenance strategies are discussed.
Maintenance Plans in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management
The Maintenance plan lines of type “Time” are used for scheduled maintenance at a predefined period. Maintenance Plans may be associated with assets, asset kinds, functional locations, or functional location types, but they must be created first.
A maintenance plan may have numerous lines of maintenance. The maintenance plan line specifies the kind and frequency of maintenance jobs. There are two sorts of lines in a maintenance plan:
- Time
- Counter
Time & Counter
Maintenance plan lines of type “Time” are used for scheduled maintenance that occurs at a predefined time period. Maintenance plan lines of type “Counter” are used to schedule or perform reactive maintenance on assets depending on their counter registrations. To begin, you establish the maintenance plans necessary for your preventive maintenance activities and specify the asset types, asset classes, asset classes, functional location types, and functional locations that should be associated with each maintenance plan. If necessary, you may add maintenance plans to an asset or functional location using the All assets > pick asset > Asset maintenance plans FastTab or All functional locations > select functional location > Maintenance plans FastTab. When you add a maintenance plan to asset types or functional location types, additional assets or functional locations created using those asset types, or functional location types are immediately added to the maintenance plan.
The relationship between a maintenance plan and its start date will be the current date, which may need modification. Our professional consultants at Dynatuners react quickly to client demands through customer relationship management, business automation, complex integration, or performance reporting.
Maintenance Plans Walkthrough in Dynamics 365
Set Up Maintenance Plans
Step 1
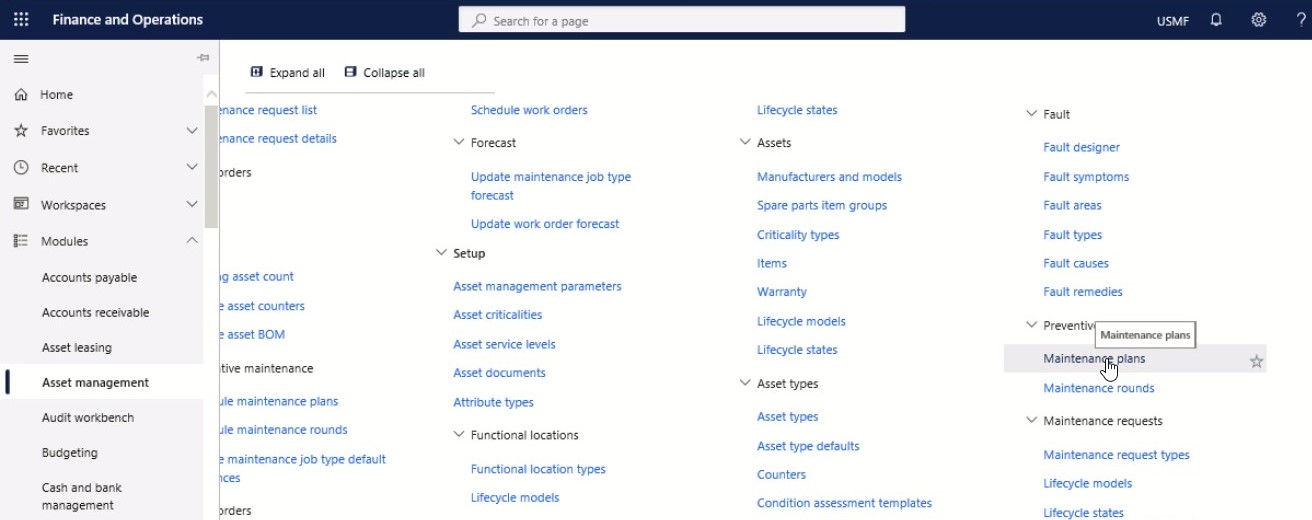
Navigate to Asset management > Setup > Preventive maintenance > Maintenance plans.
Step 2
Select New.
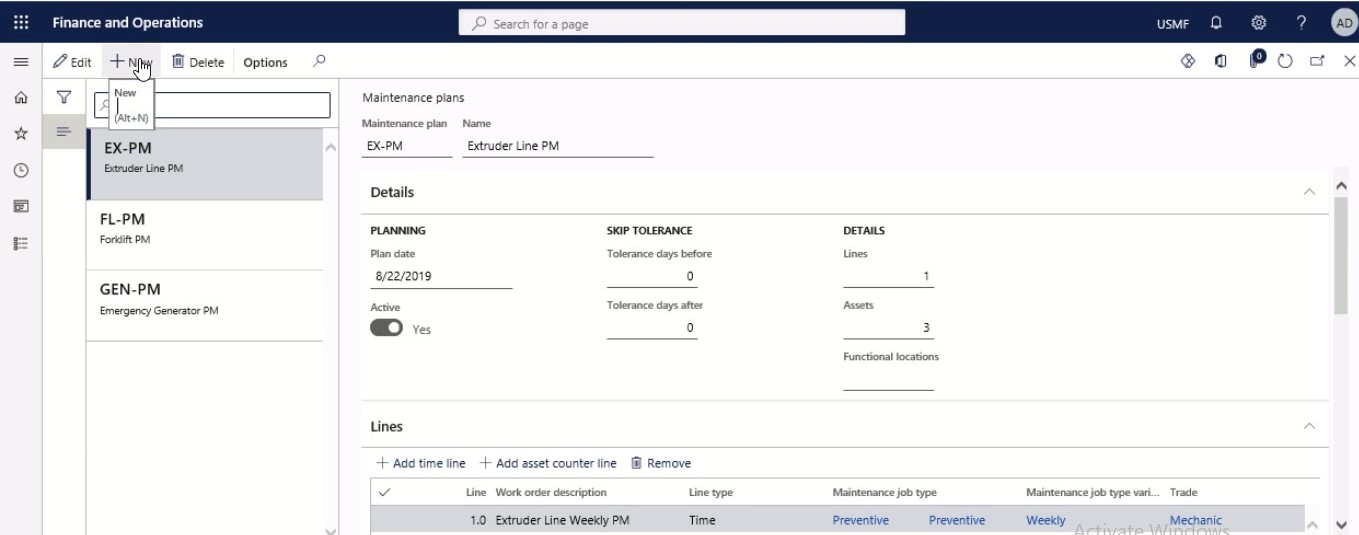
Step 3
Fill in the Maintenance plan field, and a name in the Name field.
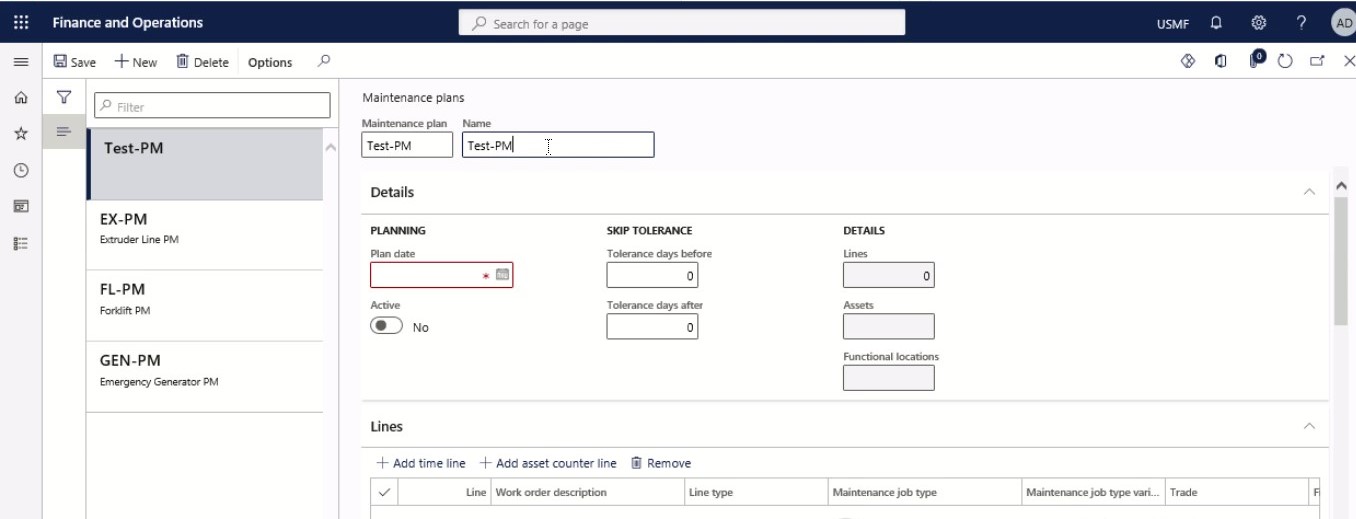
Step 4
In the Plan date field and select the start date from which planning can be done on the maintenance plan.
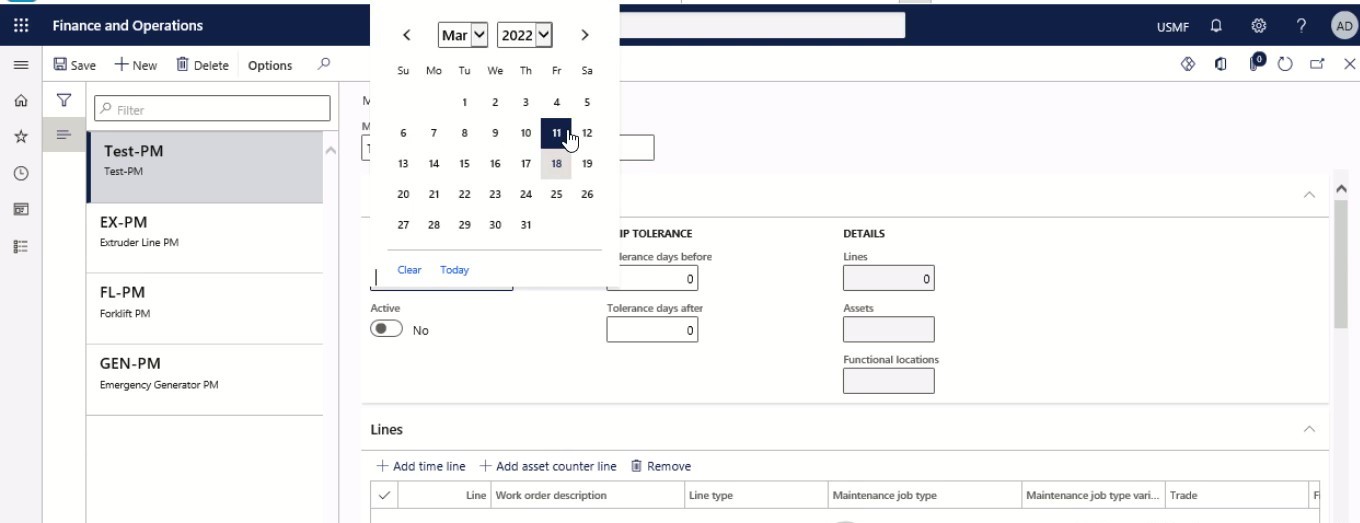
Step 5
Select “Yes” in the Active toggle button.
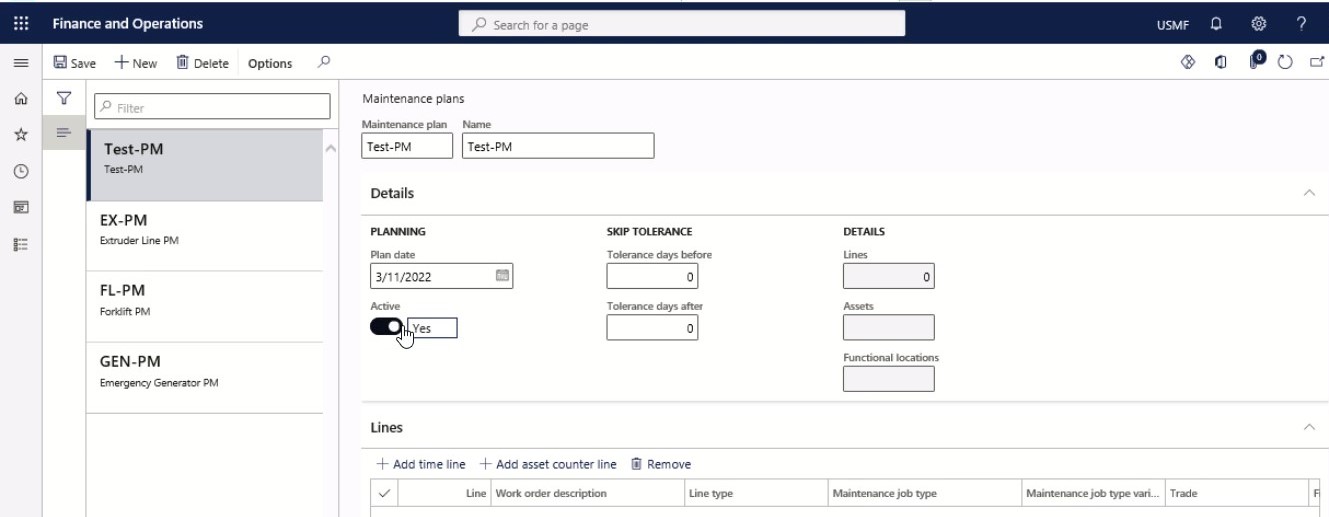
Step 6
Insert the number of days in the Tolerance days before field.
Step 7
Insert number of days in the Tolerance days after field.
Step 8
The fields in the ‘DETAILS’ group show number of maintenance plan lines set up on the maintenance plan, and the number of Assets and Functional Locations related to the maintenance plan.
Step 9
Click Add timeline or Add asset counter line to create a new maintenance plan line on the Lines FastTab.
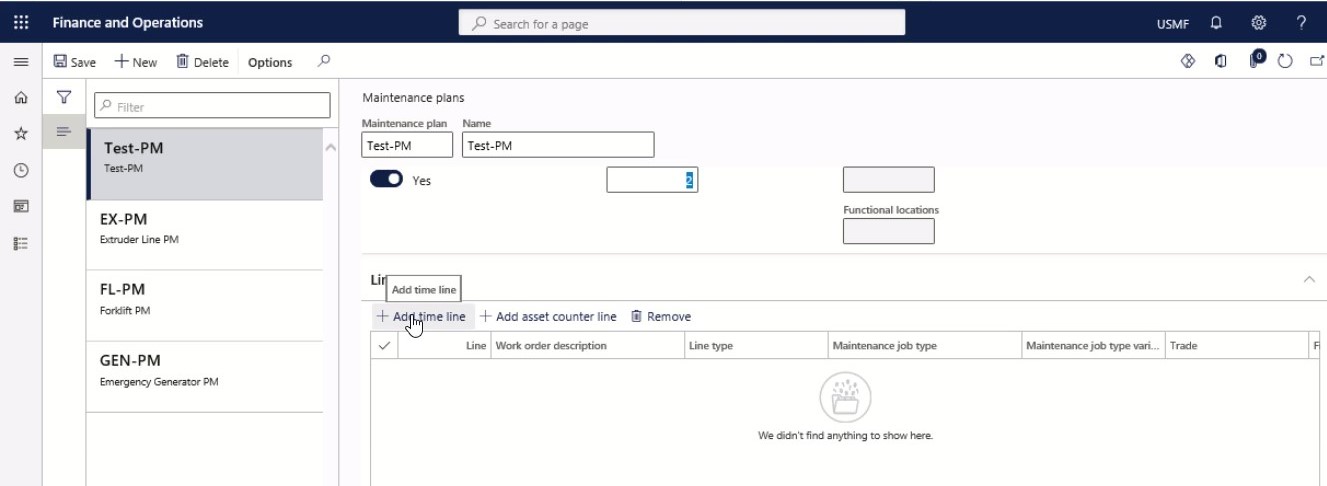
Step 10
Insert a description for the line in the Work order description field.
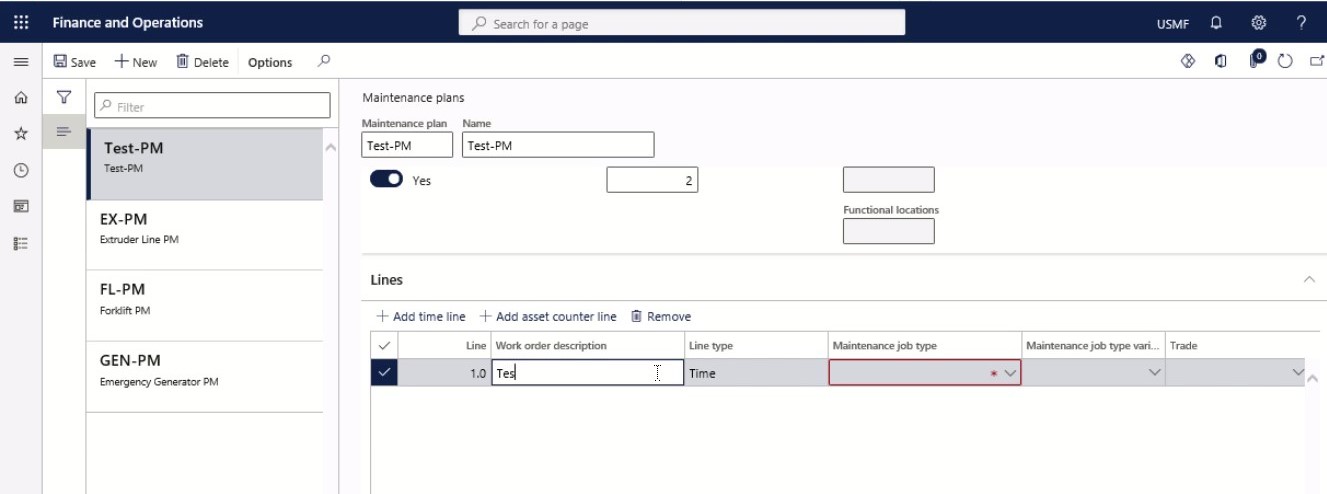
Step 11
In the Maintenance job type field, select the job type to which the maintenance plan line is related.
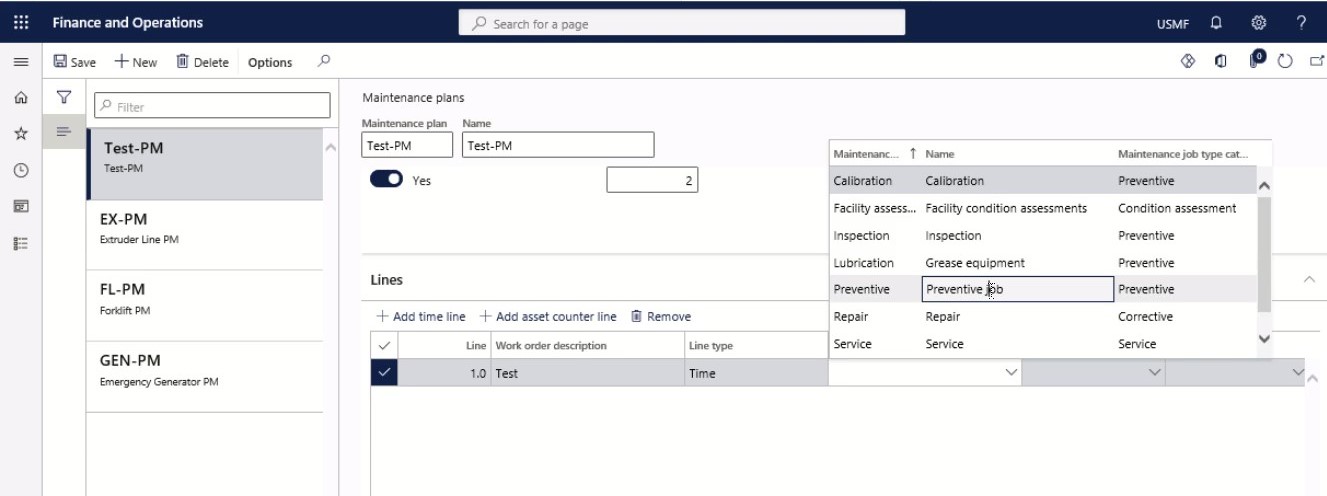
Step 12
Now in the Maintenance job type variant and Trade fields, select the variant and trade-related to the maintenance job type.
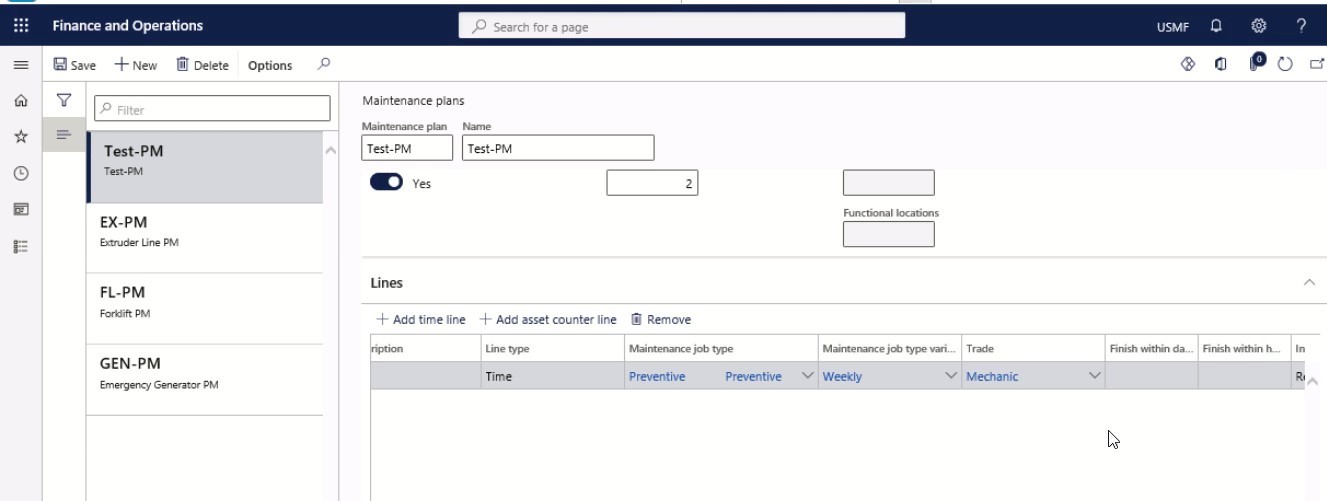
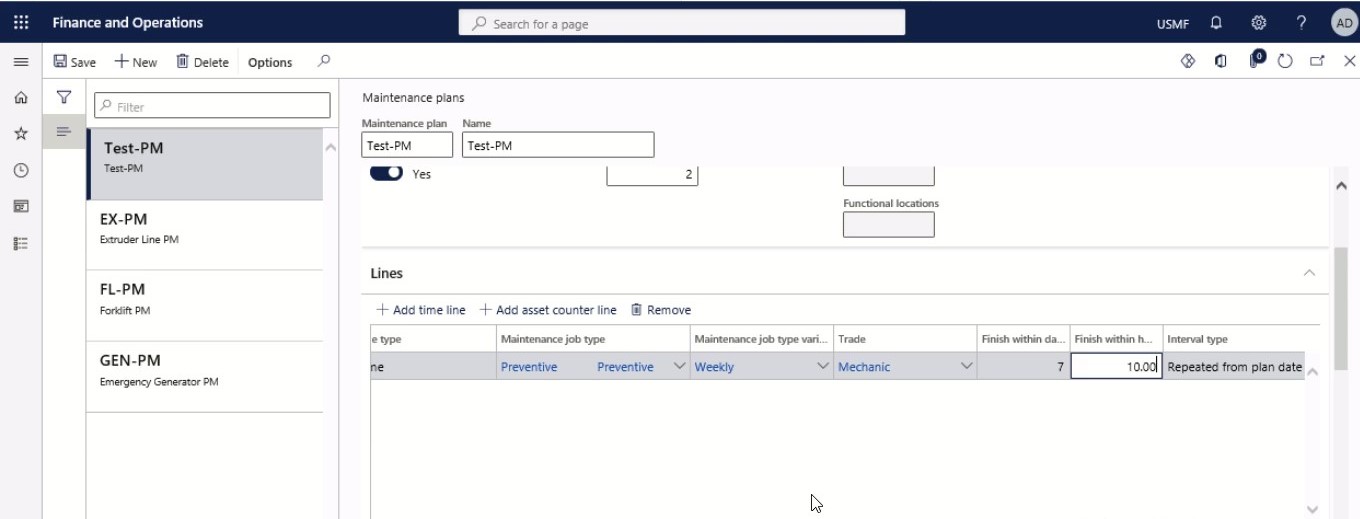
Step 13
In the Finish within days and Finish within hours fields, you can insert the expected end date in days or hours.
Step 14
In the Interval type field, select the type of interval to be used on the maintenance plan line.
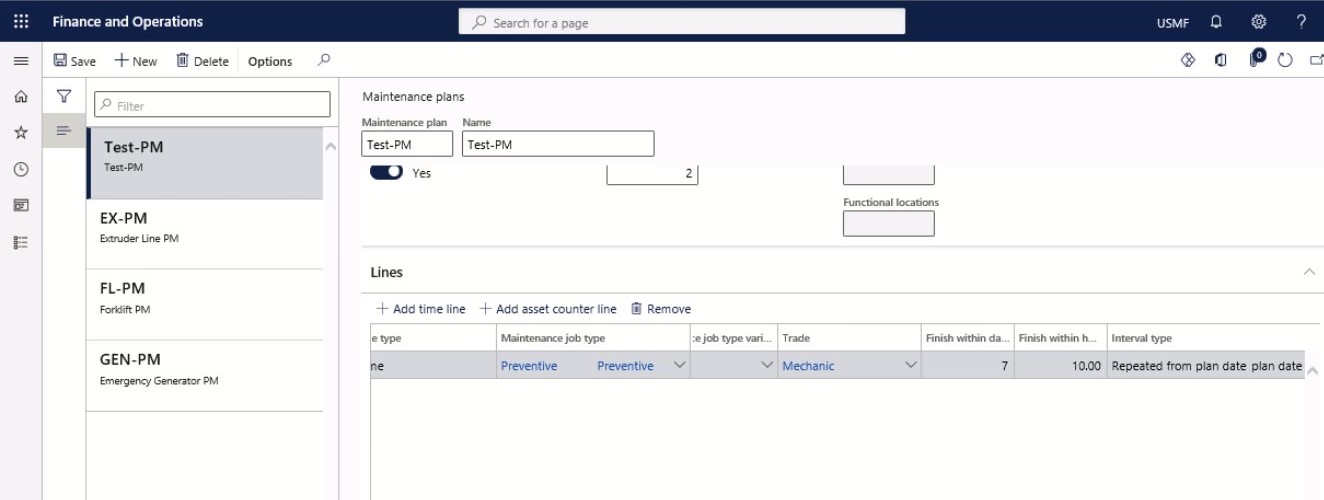
Step 15
Select the period type related to the period frequency.
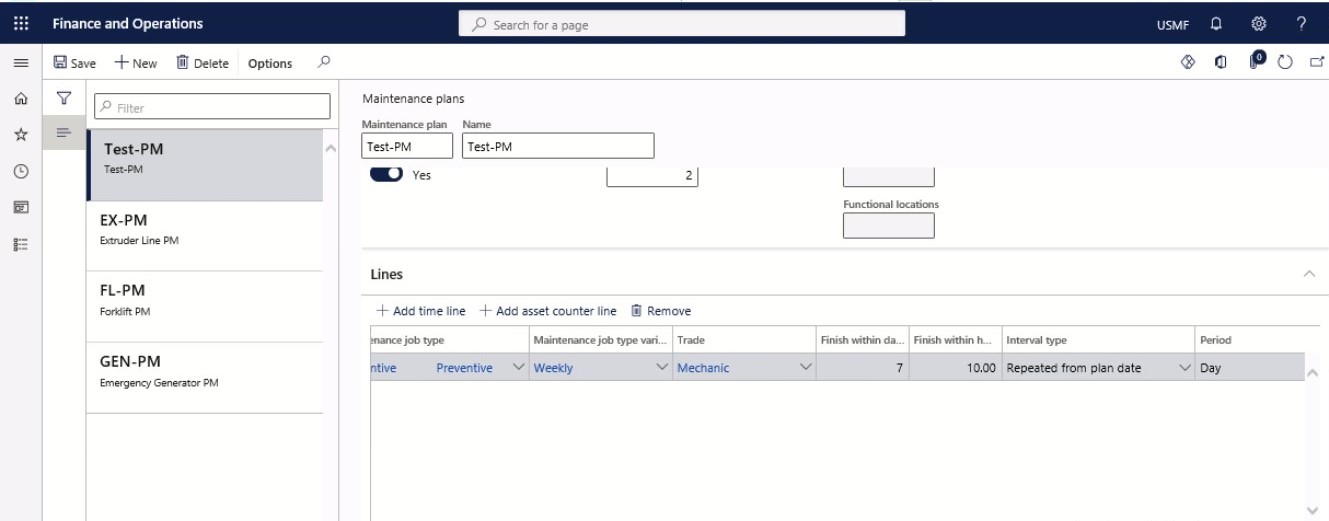
Step 16
In the Period frequency field, insert the number of times the line should be used for planning preventive maintenance jobs.
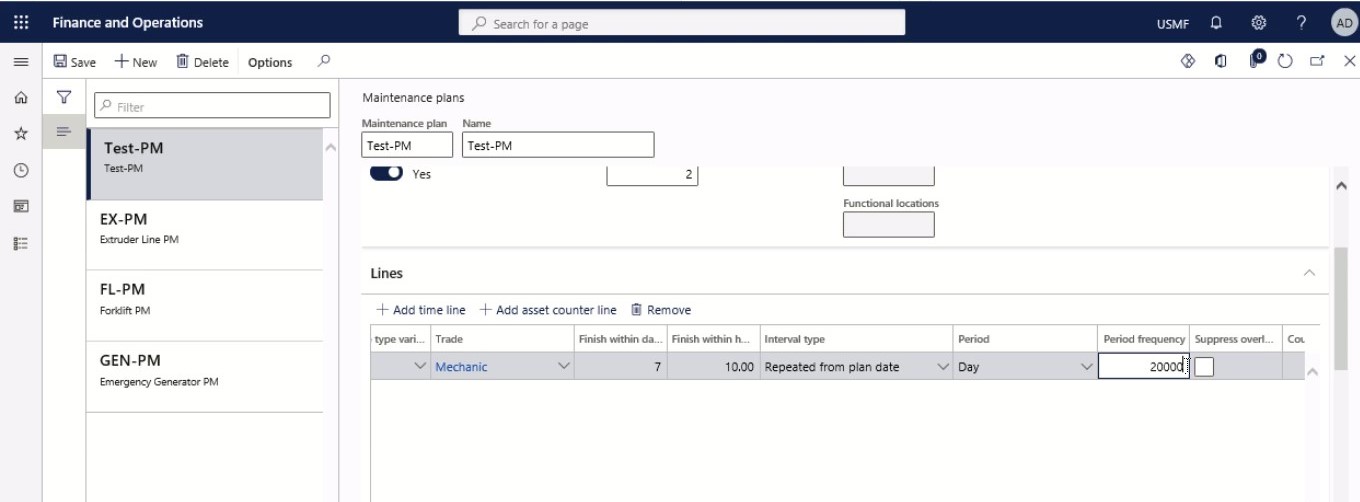
Step 17
Select the check box to delete maintenance schedule entries created on the same date. The Suppress overlapping maintenance jobs check box relates to time-based as well as counter-based line types.
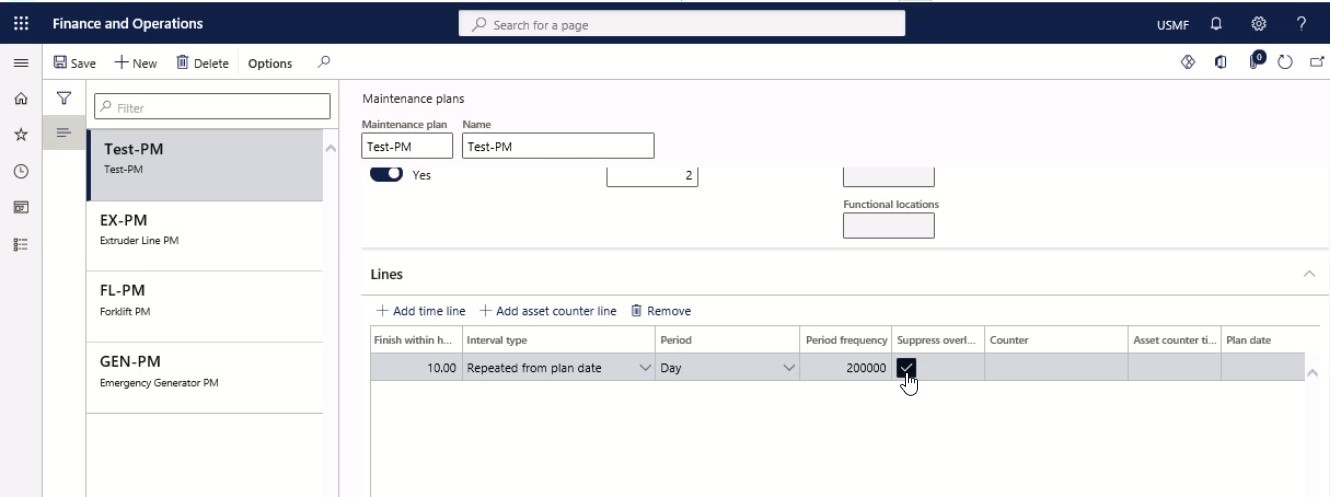
Step 18
Select the counter type to be used on the line. The Asset counter time fence in the day’s field only relates to counter-based line types. Insert a number that defines how many days back counter registrations are checked when maintenance plan scheduling is done.
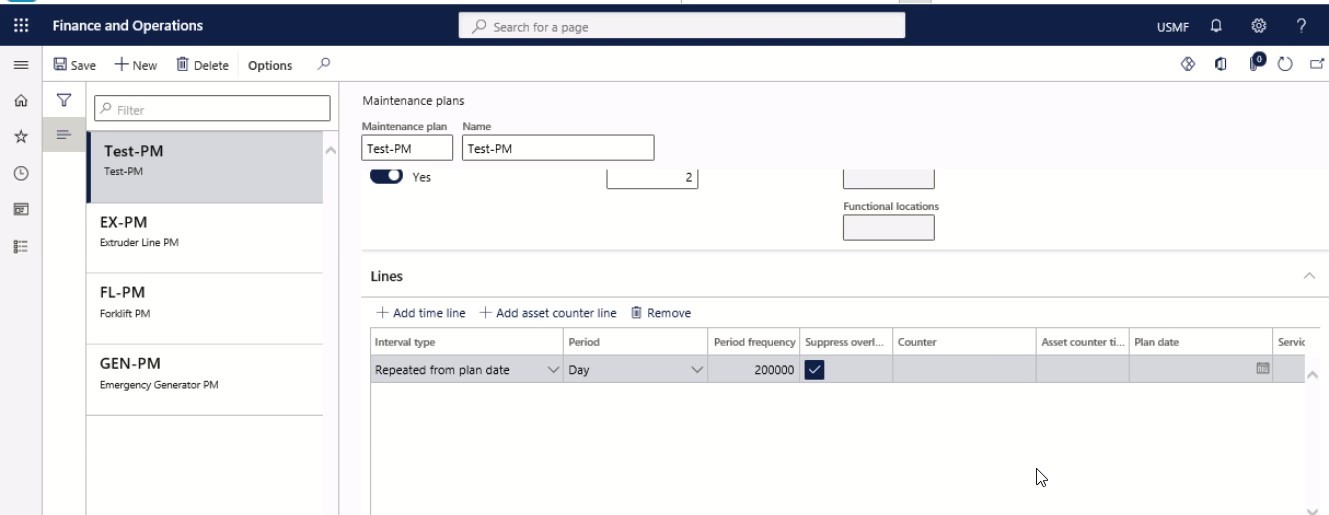
Step 19
The plan date field only relates to time-based line types. If the maintenance plan line has another planning date than the entire maintenance plan, select a date in the Plan date field on the line.
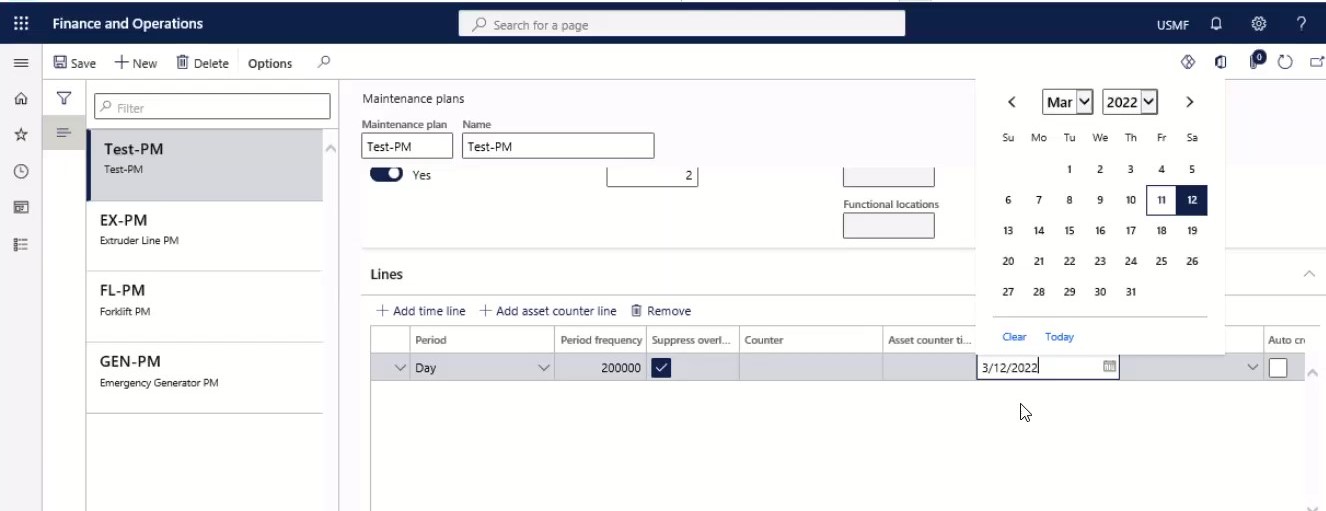
Step 20
In the Service level field, you can select a work order service level.
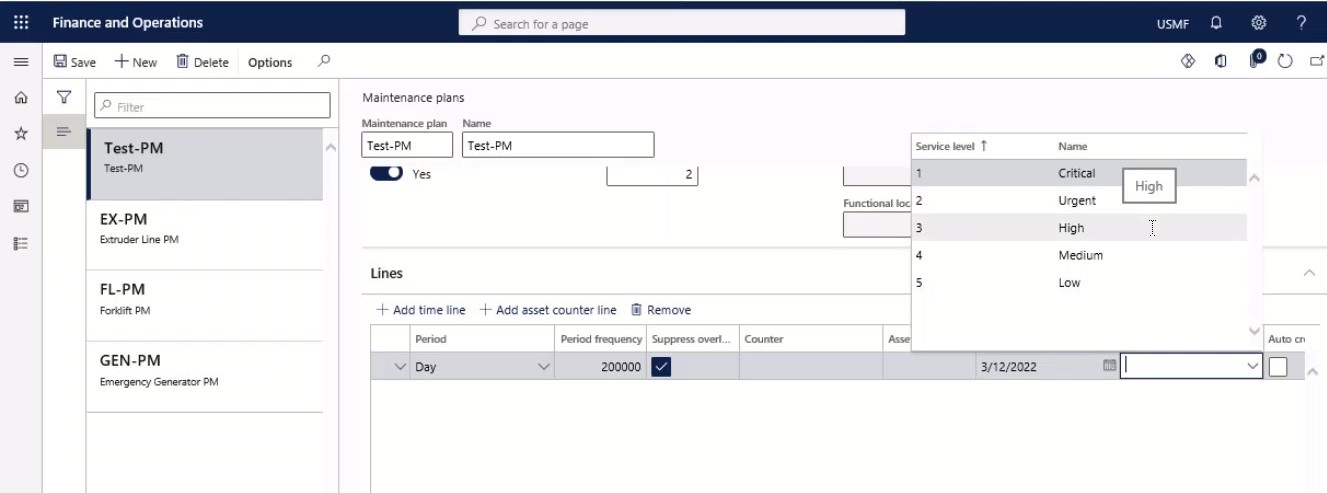
Step 21
Select the Auto create check box if you want a work order to be automatically created according to the selected maintenance plan line when scheduling maintenance plans.
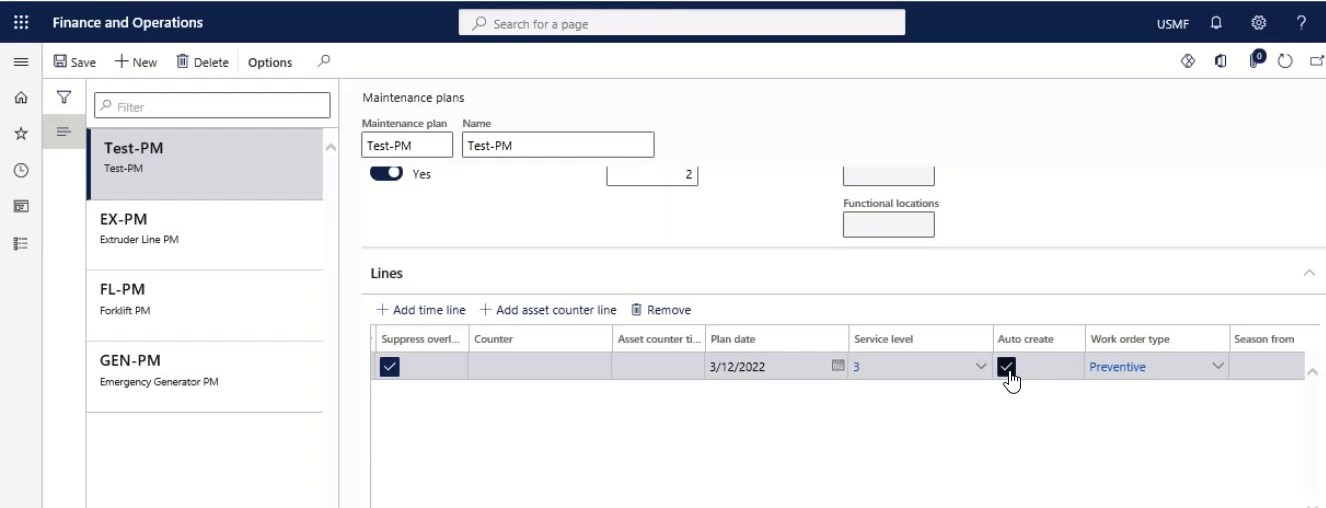
Step 22
If you have selected the Auto create check box, you can select a work order type for the auto-created work order in the Work order type field.
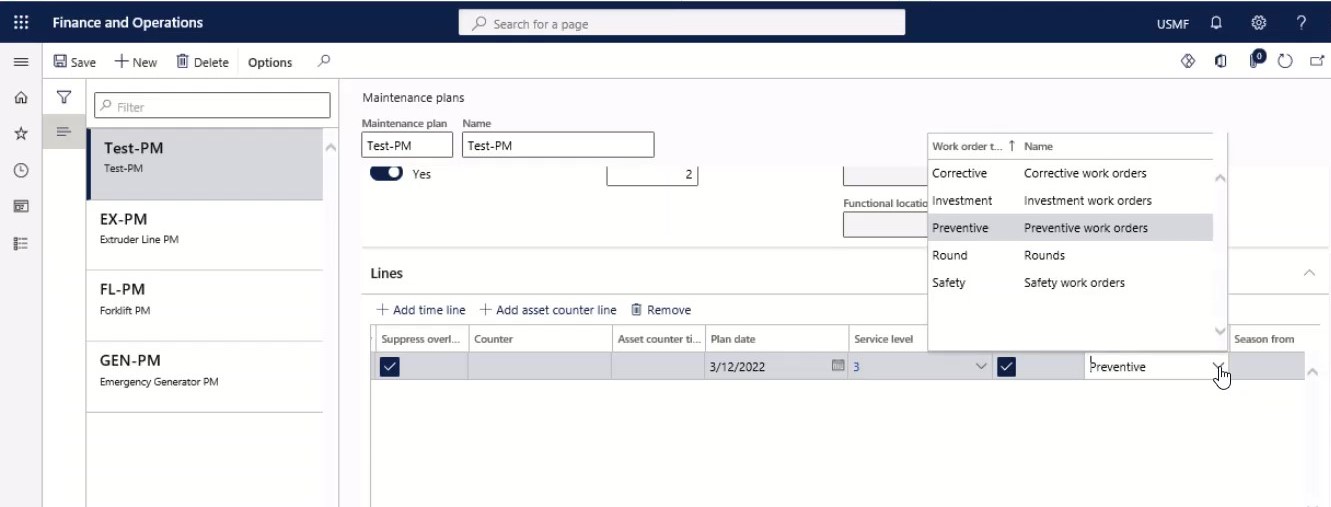
Step 23
Use the Season from and Season to fields to create a repeated time-based maintenance plan line within a 12-month period.
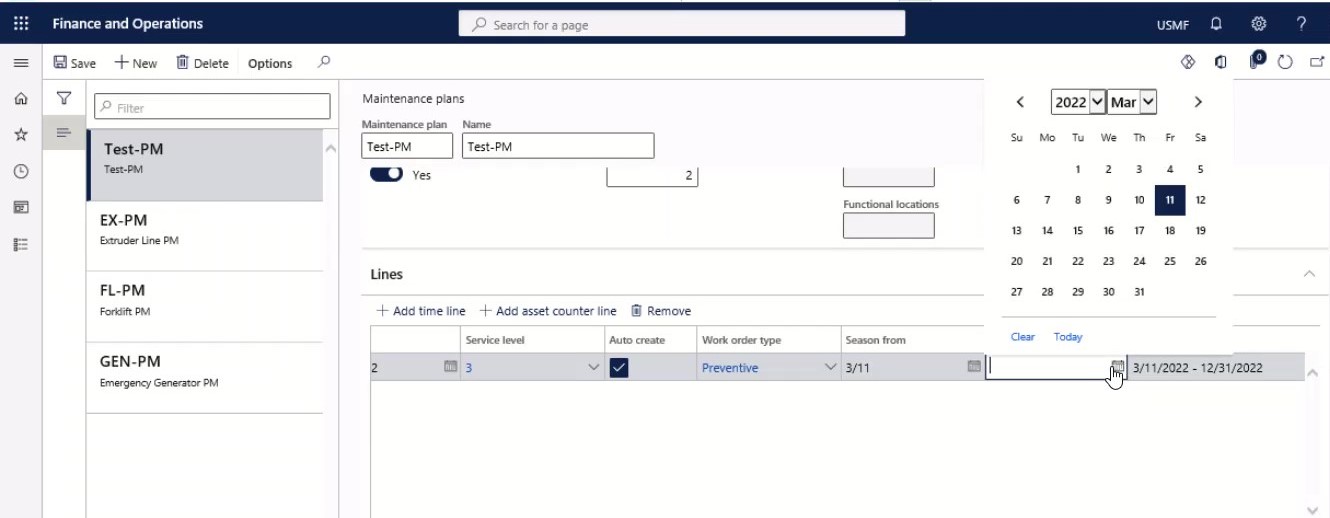
Step 24
In the Resulting period field, the current period to be repeated is shown.
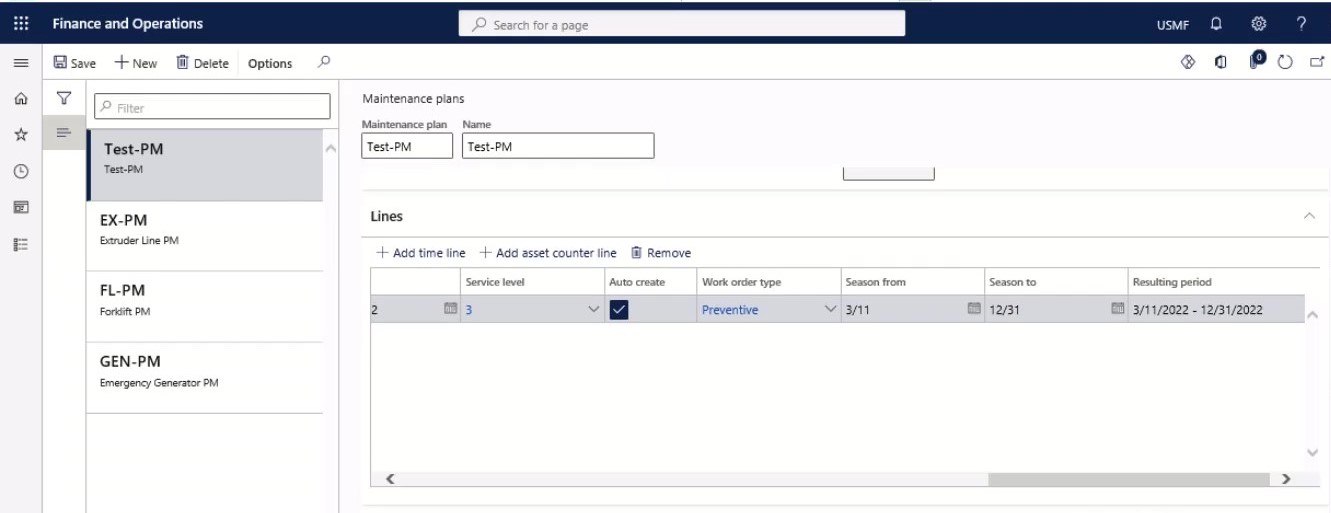
Step 25
Select the assets that should be related to the maintenance plan on the Assets FastTab.
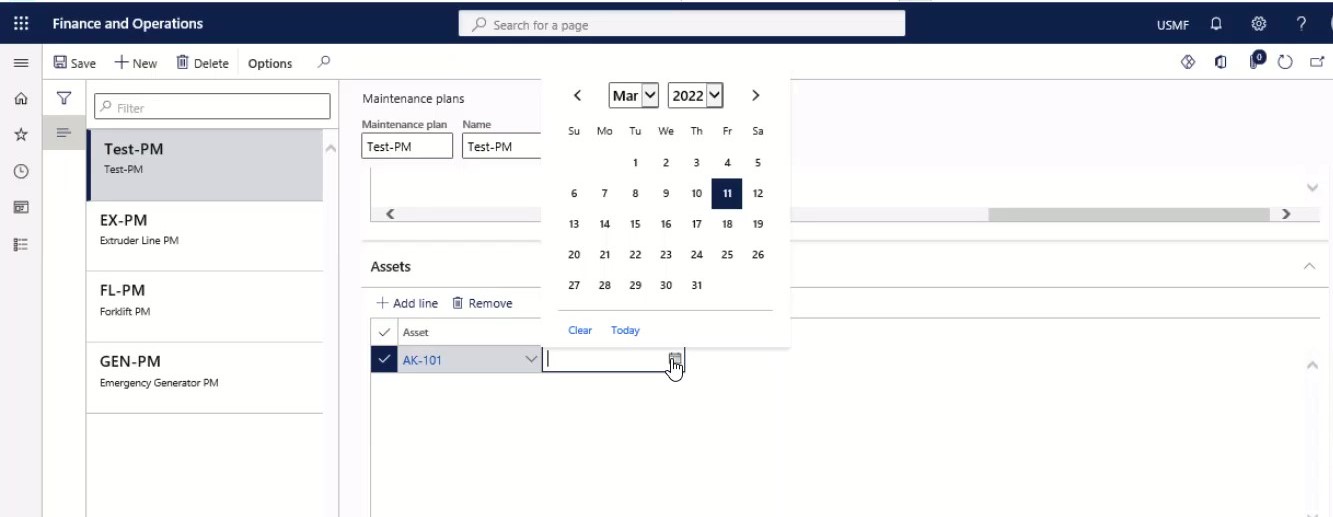
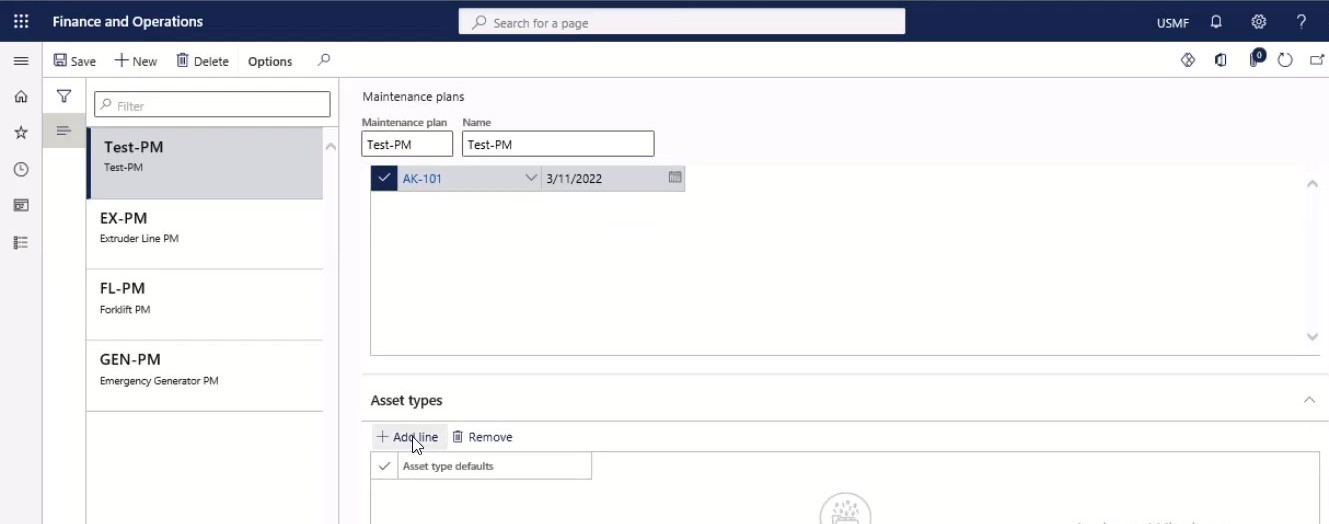
Step 26
Select the asset types that should be related to the maintenance plan on the Asset types FastTab.
Step 27
On the Functional locations FastTab, select the functional locations that should be related to the maintenance plan. If required, you can specify the setup by choosing a related asset type, manufacturer and model.
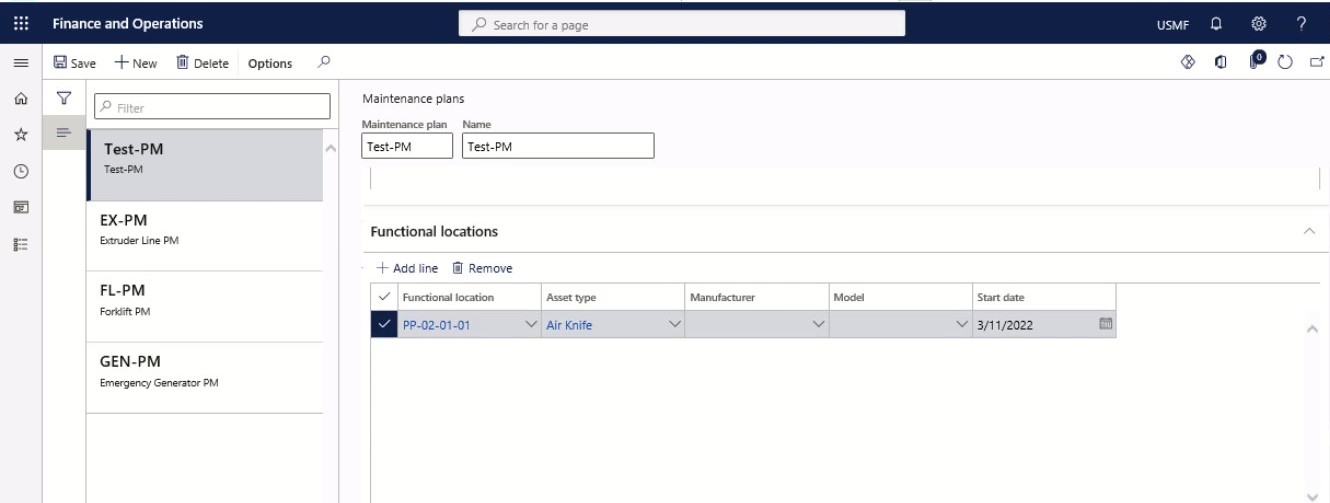
Step 28
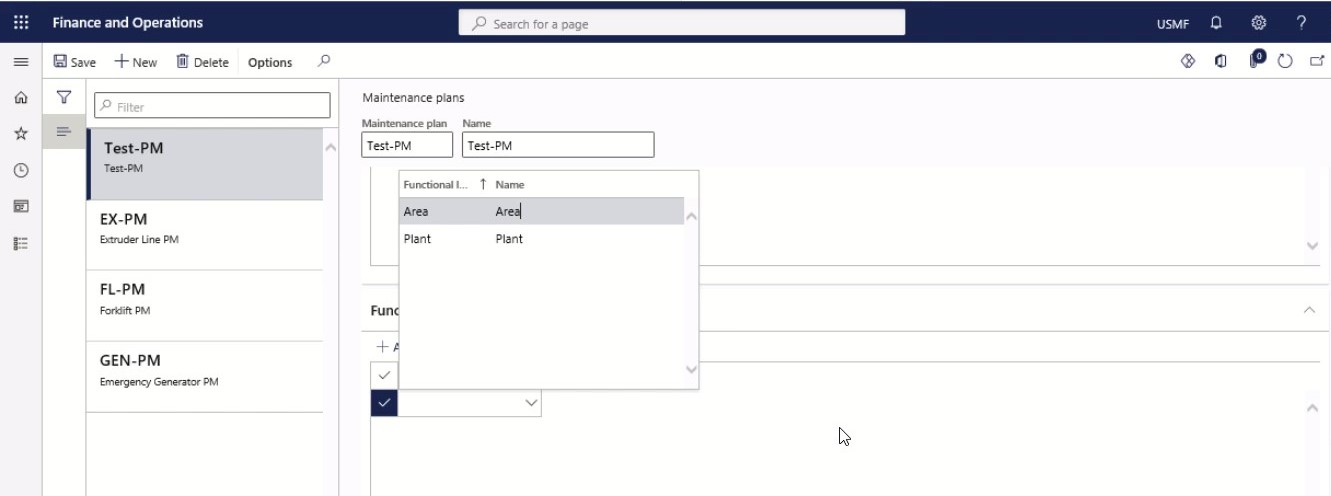
On the Functional location types FastTab, select the functional location types that should be related to the maintenance plan.
SUMMARY
Maintenance plans may be linked to assets, asset types, functional locations, or functional location types, but they must first be generated. The maintenance plan line defines the kind and frequency of maintenance activities. By following the procedures outlined above, you will be able to create maintenance plans in D365.
The Impact of Maintenance Operations on Supply Chain Management
Delays in any part of the supply chain may create substantial difficulties and lead to overall supply chain delays. One area that is sometimes ignored yet is critical in preventing the supply chain from collapsing is maintenance management. You may link maintenance operations to every point in your supply chain in one way or another. Whether in transportation, manufacturing, or storage, a single maintenance team’s failure has repercussions across the supply chain. In that light, let us discuss these more in-depth:
Transportation
Transportation is a critical component of every supply chain, whether it’s transporting raw materials to a warehouse or delivering completed goods to a customer. To ensure that this link in the chain operates without glitches, a significant amount of maintenance work must be performed behind the scenes. To begin, to deliver materials/goods to a specified location on schedule, your means of transportation must be capable of enduring the journey without experiencing a major failure. This is the point when you hope that the management of the ship, train, aircraft, and fleet have done their bit to guarantee a successful delivery. Second, it is fairly uncommon for specific materials/products to need unique transportation circumstances. The most apparent example is refrigeration. Thus, a breakdown of routinely maintained assets might jeopardize an order and result in severe delays in your supply chain.
Production
If there is one point in the supply chain where maintenance receives enough acknowledgment, it is on the production floors of the majority of operational facilities. With this in mind, maintenance managers are gradually shifting their focus to proactive maintenance. While more ambitious businesses may attempt to adopt complete productive maintenance in order to avoid unexpected downtime, a typical facility will often be satisfied with a preventive maintenance approach.
Warehousing and Storage
At some point in the supply chain, whether it is raw materials or completed goods, something will almost certainly need to spend a night or two securely housed in a warehouse.
Customer Contact
If the business is not properly maintained, a slew of additional issues might arise. This becomes much more critical if the product must be stored in a certain environment (temperature/light/humidity). As a result, maintenance is intrinsically linked to each stage of the supply chain. While each industry may have unique maintenance requirements, it’s fascinating to see how proper critical maintenance is to maintain a healthy supply chain.
SUMMARY
You can connect maintenance to any point in your supply chain. A maintenance team’s failure affects the whole supply chain. Maintenance managers are increasingly focusing on preventive care. While each business has its own maintenance needs, it’s amazing how vital adequate maintenance is to a successful supply chain.
Choosing the Ideal Maintenance Strategy for Your Equipment and Employees
Each strategy offers a number of advantages and disadvantages. Having said that, implementing an efficient maintenance plan remains a critical component of any facility’s operations. Indeed, selecting the appropriate approach is highly dependent on the unique characteristics of your firm. Preventive maintenance is almost always the best course of action.
Corrective maintenance may make more sense for institutions with limited finances or less safety issues. However, equipment maintenance is not binary; the most successful approach will consist of several components. Combining techniques enables you to determine your optimal maintenance plan most efficiently. Whichever technique you use, every firm will profit from technology. Dynamics 365 enables you to streamline the decision-making process. Additionally, it enables you to include data from critical modules while performing maintenance operations. As a result, you’ll be able to make more informed choices, expedite maintenance activities, and guarantee that important assets and people are secure at all times. D365 solutions may help your maintenance operations become more intelligent.
|
Sr. |
Industry Insights related to Maintenance & Scheduling | ||
| Factor | General Ratio | Industry Practice | |
|
1. |
Average “wrench time” (maintenance efficiency) | Generally 25 – 35% | Leading practice is more than 60% |
|
2. |
Maintenance Overtime | average in the US: over 14% | Leading practice is below 4%) |
|
3. |
Reactive maintenance | Reactive maintenance results in higher maintenance cost
|
|
Note: Factors to consider related to planning and scheduling are based on averages across all industries.
SUMMARY
Preventive maintenance is usually always ideal. D365 solutions can help you improve maintenance operations. You can use technology to speed up decision-making. As a consequence, you can speed up maintenance and protect vital assets and people.
At Instructor Brandon | Dynatuners, we always seek innovative methods to improve your competitiveness and suit your Microsoft Dynamics 365 requirements. Our offerings are founded on defined procedures, industry experience, and product understanding. If you’re interested to consult with our specialists on how to resolve maintenance issues, don’t hesitate to Contact Us.
[sc_fs_multi_faq headline-0=”h2″ question-0=”What is included in a maintenance plan? ” answer-0=”A maintenance plan identifies the assets that must be maintained (such as roofs, windows, pumps, boilers, etc.). It details maintenance tasks (such as inspecting, cleaning, adjusting, re-aligning, lubricating, etc.). Additionally, it specifies the periods at which each asset must be maintained (such as weekly, quarterly annually, etc.). Finally, it indicates the skill levels required for each maintenance job. ” image-0=”” headline-1=”h2″ question-1=”What is the definition of a maintenance management plan? ” answer-1=”Essentially, the ideal maintenance management strategy enables a business to maintain its assets while keeping costs and time under control. This aids in achieving optimal efficiency throughout the procedure. Businesses that have a maintenance plan in place have a higher chance of keeping expenditures under control. ” image-1=”” headline-2=”h2″ question-2=”What characteristics distinguish an effective maintenance planner? ” answer-2=”A good maintenance planner has good communication skills, a good understanding of maintenance and workflow procedures, and a firm grasp of technological concepts. They are also concerned with maintaining the efficiency of facilities via their planning and scheduling strategies. ” image-2=”” count=”3″ html=”true” css_class=””]
 4986
4986