Microsoft Dynamics 365 Developer (F&S) Training Series, Supply Chain and Logistics Management
Concerned about invoicing errors and damaged goods? Improve transparency in shipping processes with handling fees using Dynamics 365

Improve Transparency in Shipping Processes to avoid Invoicing Errors
Supply Chain Transparency | Freight Charges | Purchase Orders | Sales Order | Shipment ID | Invoicing
Are you concerned about invoicing errors and damaged goods? Do you want to improve your invoicing and shipping processes?
With online shopping’s ever-present speed and ease, few consumers pause to consider how many tangible shipping touchpoints are needed to get a product to their house. There is a lot more than simply delivery expenses involved in shipping and handling, so it’s critical to know that before asking, “How much does shipping cost?” Shipping and handling costs may be tricky since there are many variables to consider.
What are shipping and handling?
Shipping and handling are when an order is prepared and packed, then sent to the client. Shipping and handling costs are often listed as an additional charge on the item price and any taxes. This involves logistical expenses such as personnel, packaging materials, inventory storage, transportation, and delivery.

SUMMARY
In shipping and handling, there is a lot more to consider than just delivery costs and invoicing. This service takes care of personnel, packing materials, inventory storage, transportation, and delivery. On top of the item price and any taxes, shipping and handling fees are often stated as an extra charge.
Shipping vs. Handling: What’s the Difference?
While many consider shipping and handling to be the same thing, others may be perplexed.
In shipping, postage and other transportation costs are included to get a product from a shipping carrier to the final customer. In addition, surcharges, fuel costs, and other expenses associated with the distance traveled and the delivery timeframe selected are all included in this price.
So, what is a handling fee? To determine that, the following terms are used: inventory collection expenses, packing costs, shipping costs, and any other warehouse movement costs. Read more on procurement invoicing at our website.
To put it another way, handling fees cover a large portion of the total order fulfillment cost. The handling costs go up accordingly when additional contact points are needed, such as kitting and assembly, gift wrapping, customizing, or inserting items.
One of the most challenging challenges e-commerce businesses have is determining how much to charge for shipping and handling. The final aim is to find a happy medium between making a good profit and not pricing too many online consumers out of the market, leading them to cheaper rival sites.
SUMMARY
Order fulfillment expenses include invoicing, shipping, postage, and other transportation charges. Handling expenses rise when more touchpoints are required, such as kitting and assembly, gift wrapping, customizing, or inserting goods. The goal is to strike a balance between earning a decent profit and pricing away too many consumers.
Billing and Invoicing Errors
The volume of transactions you handle each day may have a significant effect on your bottom line. Because of this, a large number of businesses depend on freight audits to ensure compliance while minimizing losses and maximizing income.
Defense is always better than attack when it comes to minimizing the damage caused by freight billing and invoicing mistakes.
Freight Billing Error #1 – Shipper Inaccuracy/Errors on the Bill of Lading
A bill of lading is the comprehensive list of cargo details provided by the carrier to the consignee. When it comes to shipping, a bill of lading is a critical document since it gives drivers and carriers all the information they need to complete the shipment’s journey. Thus, it has the function of serving as a receipt of sorts.
A mistake in the carrier, contact information, or weight information on your bill of lading may lead to incorrect cargo information being sent to your shipper, which can have a variety of adverse outcomes, including:
- Inability to deliver on time.
- Losing the power to place a cap on a company’s liabilities.
- Loss of P&I insurance protection.
- Failure of the charterer’s indemnification rights.
SUMMARY
A bill of lading is a detailed summary of cargo information given to the consignee by the carrier. It provides drivers and pages with all the information they need to complete the shipment’s trip correctly. Incorrect cargo information being supplied to your shipper due to a mistake in the carrier, contact information, or weight information on your bill may have several severe consequences.
Freight Billing Error #2 – Detention Errors
A penalty cost is called a detention mistake applied to the shipper’s account if the carrier’s pick-up schedule is delayed beyond the agreed-upon period. Carriers cannot use their equipment because of per diem costs the shipper pays when equipment is kept for longer than the agreed-upon period. In addition, a set daily fee (per container, per day) will be added to the freight account if the equipment is not returned.
Shippers and receivers pay driver detention costs when the time it takes to load and unload the vehicle exceeds the time the driver must wait at the origin or destination. Delaying other drivers reduces their legally mandated 11-hour driving limit, raises accident chances by 6.2% (U.S. DOT), and may significantly negatively impact a driver’s professional standing. This fee is intended to make up for the inconvenience caused to drivers and is charged hourly.
Check your bills carefully to ensure the agreed-upon detention error rate is adequately carried through to avoid overcharging or undercharging costs.
SUMMARY
If the carrier’s pick-up plan is delayed over the agreed-upon time frame, a penalty known as a detention error is charged to the shipper’s account. This fee is paid on an hourly basis and is designed to compensate drivers for the difficulty they have experienced.
Freight Billing Error #3 – Accessorial Charges
Accessorial costs are fees that the carrier charges the shipper for freight services that go above and beyond the carrier’s regular pick-up and delivery routes. These are just a few examples.
Liftgate service may be used when a vehicle has to be raised a few feet off the ground to make moving goods easier. Inside-delivery occurs when a package is delivered to the front entrance of a residence or business.
Clear communication between the shipper and the recipient is the best method to prevent any kind of penalties on your freight account. Inquire about the location’s type, appearance, features (if any), and which vehicle would most effectively complete the cargo. This will assist in minimizing any invoicing problems the carrier may run into throughout the shipping procedure while also reducing the possibility of a slew of surprise charges for everyone involved.
SUMMARY
Accessorial expenses are fees charged to the shipper for freight services not included in the carrier’s standard pick-up and delivery routes. For example, lift gate service is utilized when a vehicle has to be lifted a few feet off the ground to make transferring items simpler.
Freight Billing Error #4 – Overlooking Discounted Rates
As a result of these efforts, your contract and freight teams have worked hard to secure advantageous conditions for your company. By maintaining your agreements on file while auditing your invoice and connecting all the connections between your contracts and invoices, you may avoid overlooking reduced prices between you and your third-party suppliers. The key to catching an accounting mistake early on is vigilant. If you discover a misunderstanding between your third-party vendors, you should submit a re-bill to make things right.
SUMMARY
Being attentive is essential for detecting and accounting errors early on. You should submit a re-bill if you find a miscommunication between your third-party suppliers. You may prevent spotting decreased pricing if you keep your agreements on file when reviewing your invoice numbering.
How can you figure out how much it will cost to ship something?
The shipping and handling charges are based on three significant variables. These are:
-
Handling
If you want to know how long it will take to wrap an item correctly, divide the average number of minutes by 60. This may be calculated using the following equation:
(Average time to package an item/60) x hourly wage of a team member.
This is an example of how handling costs may be computed if your workers earn $15 per hour and it takes those 10 minutes to package an item:
It costs $2.40 to handle 10 minutes/60 minutes, or a little more than a quarter of a cent an hour.
Use this method if you’re an entrepreneur working by yourself in an e-commerce business:
Your hourly wage equals (60 minutes on average to package an item)
-
Packaging
Products must be packaged safely, which necessitates boxes, packing materials, tape, and other items.
A good rule of thumb is to use padded envelopes and compact boxes wherever possible. This will save you money on packing costs.
-
Shipping
A parcel’s weight and size go a long way toward determining shipping costs. Shipment costs to your clients are greatly affected by the final destination. However, you may quickly and openly calculate your shipping costs by using shipping cost calculators that are readily accessible.
Putting a flat $4.99 shipping and handling charge on all items seems alluring, but it’s a bad long-term idea. In addition, shipping and handling charges may be complicated to calculate, so do it carefully rather than buy haphazardly.
To get an advantage over rivals, boost revenues, and even gain greater insight into the inner workings of your own business, it is necessary to break down and correctly calculate the amount you should charge for shipping and handling.
SUMMARY
Divide the average number of minutes by 60 to determine how long it will take a team member to package an item. When using padded envelopes and compact boxes, it’s a good rule of thumb to utilize them wherever feasible. Calculating shipping and handling fees may be complicated, so take your time.
The benefits and drawbacks of charging your clients the handling cost
Quotes from built-in shipping options may have handling costs added to them. Purchases utilizing expedited shipping options need extra attention and take precedence in the fulfillment process. Therefore some merchants prefer to charge a handling fee for such orders. In addition, customers may be charged a handling fee if orders take longer to pack because of the destination country or area.
Merchants often tack on a handling fee:
- The cost of shipping supplies (such as boxes, tape, and labels) will be covered.
- The cost of preparing incredibly fragile, delicate, or perishable goods for transportation will be off.
It’s a double-edged sword to charge customers for shipping and handling. Simplifying pricing, covering costs, and increasing cross-selling possibilities are all possible outcomes of doing so.
-
Simplifies Pricing
Shipping, packing materials, and labor expenses are all included in the final product price without handling fees. Thus, the pricing approach for individual products is simplified by having handling costs as a subtotal line.
-
Covers Expenses
By charging for the time, effort, packing, and shipping of purchases, you’re making sure that all associated expenses are considered.
-
Increased opportunities for upselling and cross-selling
Increased sales volumes and total profitability may be achieved by passing on fees and other costs to consumers. Instead of paying for delivery, customers choose to spend an additional $10 or $20 on a product. There are e-commerce systems assist customers in fulfilling their minimum spending requirements by providing suggestions based on their cart and purchasing history.
Drawbacks
There are disadvantages as well to passing on handling costs to the consumer. Shipping and handling expenses are becoming an essential factor for many consumers when making online purchases. The companies who provide free delivery stand out in the minds of customers buying only on pricing. When customers know where to look for the most terrific deal online, they’ll avoid going to more expensive stores. The lower the number of page visits, the lower the chances to sell to a customer. Free shipping and handling is a standard promotional strategy used by online merchants to attract consumers. One method to drive consumers along the conversion funnel is to charge them nothing more. Free delivery, on the other hand, may have a higher cost per purchase than other options.
SUMMARY
Purchases utilizing expedited shipping options need extra attention and take precedence in the fulfillment process. Customers may be charged a handling fee or invoicing errors if orders take longer to pack because of the destination country or area. There are e-commerce systems that assist customers in fulfilling their minimum spending requirements.

What are the benefits of doing an audit on your shipping invoice?
FedEx, UPS, and DHL bills are rife with mistakes, including erroneous fees, double invoicing, and other clerical inaccuracies. It’s almost difficult to find every error by hand. However, computers driven by artificial intelligence (AI) can rapidly analyze tens of thousands of invoices and improve processes in only a few minutes. Our audit engine unearths all overcharges, inconsistencies, and service failures for all customers. The logistics team will be able to make better strategic decisions with Audit Shipment’s simple reports.
How to Calculate?
Incorrect surcharges result in an 8 percent increase in shipping expenses. Shipment companies may impose an additional fee on top of the quoted shipping cost. This charge is calculated on a sliding scale depending on the total package weight and delivered order. More than 20 carrier mistakes, such as fuel surcharges, home delivery fees, Saturday delivery fees, and others, may appear on shipping bills. Learn about duplicate shipments to help through invoicing.
|
Sr. |
KPIs for Delivery Metrics | |
| Metric | Description | |
|
1. |
Number of deliveries | The number of completed deliveries of your products or services. Typically, it is the sum of all deliveries within a month, quarter, or year |
|
2. |
On-time delivery | The number (or percentage) of deliveries carried out on time specified by the customer’s order, while the remaining figure points out late deliveries |
|
3. |
Order accuracy | The percentage of orders executed free of errors when compared against the total number of orders delivered |
|
4. |
Transit time to distance | The time drivers and couriers spend during transport from the pick-up site to the drop-off location |
|
5. |
Average time per delivery | The average time it takes to complete a delivery over a specific period. It offers insight into the effectiveness of the supply chain network and the efficiency of the planned delivery routes.
Also called the average service time metric, you calculate it by dividing the total delivery time with the number across a predetermined interval (day/week/month/quarter/year) |
Using Microsoft Dynamics 365 to keep track of sales and Invoicing
Charge codes are handy when you need to keep track of more than just line items, such as sales or purchases. For example, a purchase order may include invoicing, freight, and insurance costs, itemized individually on order. These costs may be added to the cost of goods or sent to expenditure accounts as you see fit.
You can create charges codes for Accounts receivable and Accounts payable.
SUMMARY
For all customers, Audit Shipment’s audit engine uncovers all overcharges, discrepancies, and service failures. In addition, artificial intelligence (AI)-driven computers can quickly analyze tens of thousands of invoices in only a few minutes.
Functional Walkthrough for Setting up Charge Codes
Set up charges codes for Accounts receivable
Step 1
Click Accounts receivable > Setup > Charges > Charges code.
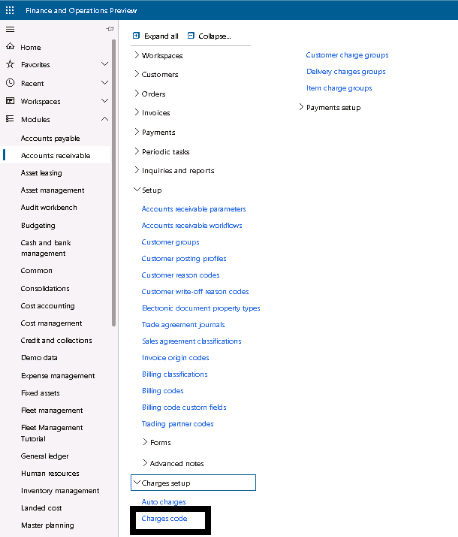
Step 2
Click New. In the Charges code field, type a code for the charge.
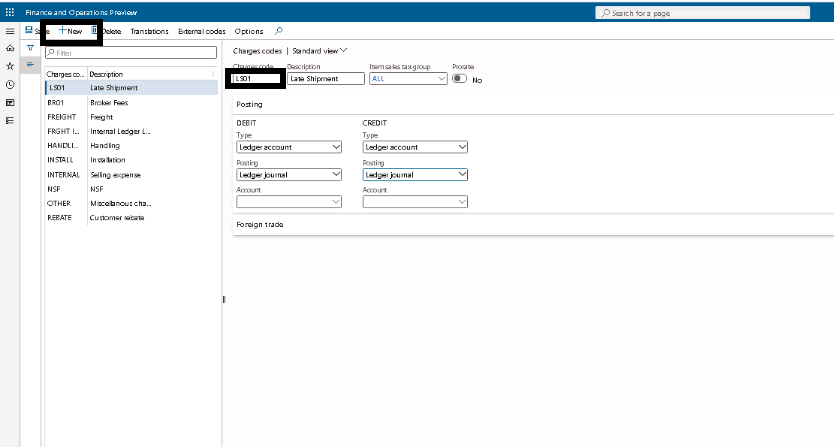
Step 3
In the Description field, type a description of the charge.
Step 4
Optional: In the Item sales tax group field, select a sales tax group.
Step 5
On the Posting Fast Tab, specify how the charge is automatically debited and credited.
Step 6
If you selected Ledger account as the debit type of credit type, specify a posting type in the Posting fields, and identify the main account in the Account.
Set up charges codes for Accounts payable
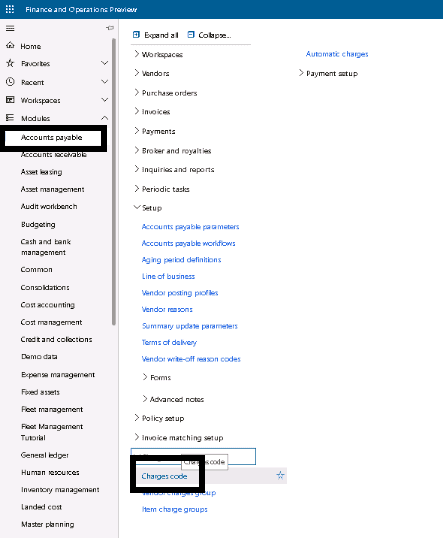
Step 1
Click Accounts payable > Setup > Charges > Charges code.
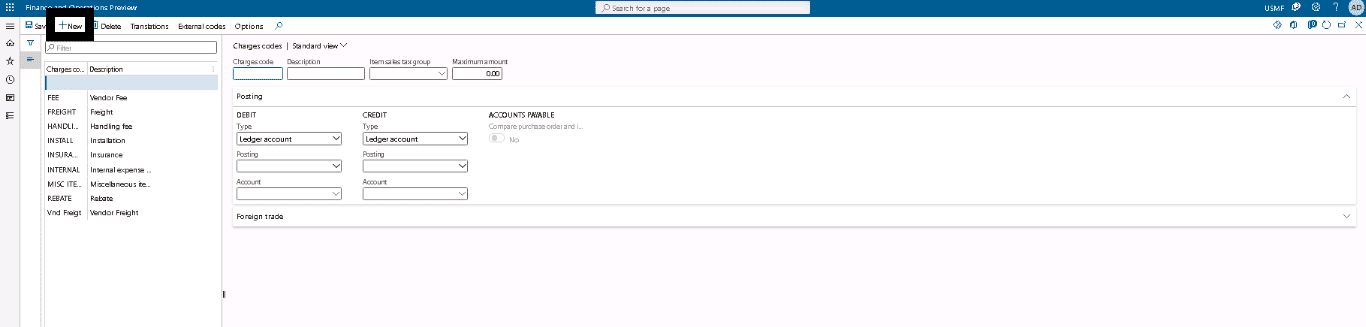
Step 2
Click New. In the Charges code field, type a code for the charge.
Step 3
In the Description field, type a description of the charge.
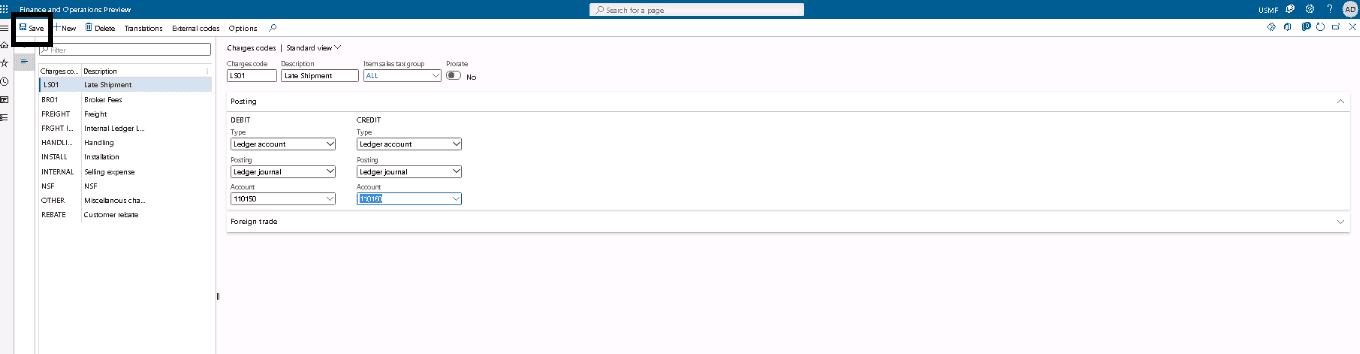
On the Posting Fast Tab, specify how the charge is automatically debited and credited.
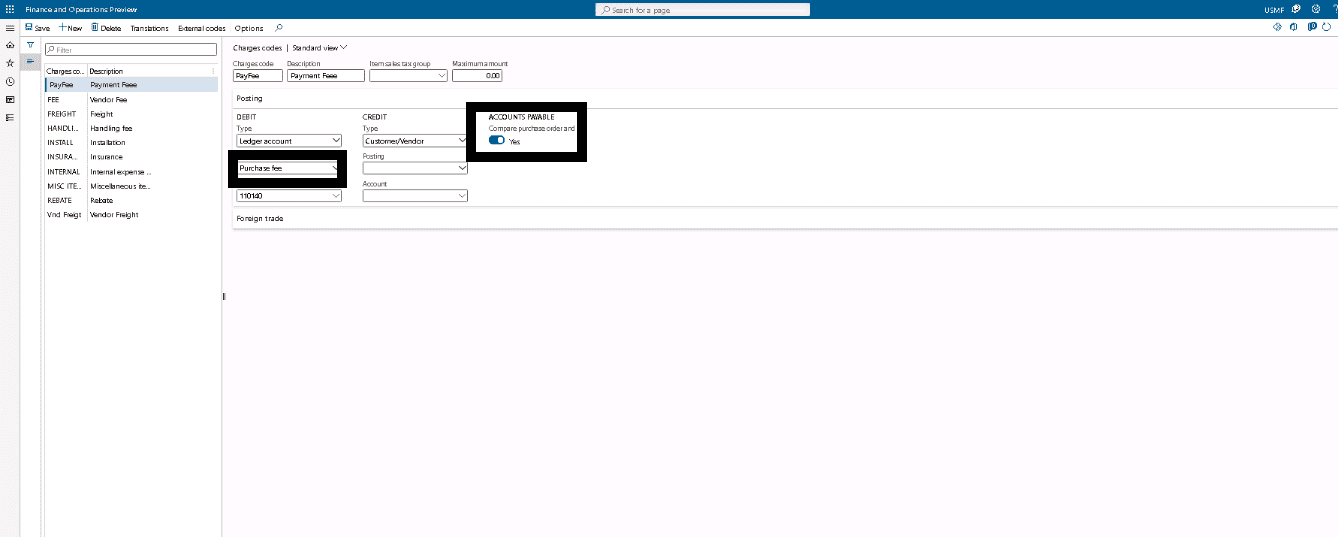
Step 4
If you selected Ledger account as the debit type of credit type, specify a posting type in the Debit posting and Credit posting fields, and identify the main account in the Debit account and Credit account fields.
Step 5
To enable the comparison of charges values for an invoice that contains the charges from the corresponding purchase order header or lines, select the Compare purchase order and invoicing values check box.
SUMMARY
Charges codes are helpful if you need to track sales or purchase amounts in addition to line items. For example, following the above steps, you can create charge codes for accounts receivable and accounts payable.
Shipping and Handling Strategy
In addition to your storage capabilities, logistics operations, and resources, your shipping and handling strategy is also influenced by these factors.
In-house vs. third-party logistics (3PL)
Instead of utilizing an order fulfillment provider, consider adopting internal warehousing, which offers you greater control over the pick-and-pack-and-ship process.
Storage space, machinery, and equipment must all be purchased, and skilled employees must be hired to assist with different order fulfillment tasks when doing in-house warehousing. A 3PL supplier, on the other hand, handles all aspects of shipping and handling for you.
Order volume and the number of SKUs
Shipping and handling are simplified for you because of the low order volume from local consumers, and you’re able to keep prices down as a result.
You may have to use an order fulfillment service if your company’s needs exceed your current skills or capacities. Remember that the more SKUs you provide, the more your 3PL provider will charge you storage costs.
A logistics solution that can expand to meet your increasing requirements will be necessary whether you’re just starting out or already have an established company. This may be achieved either via internal capacity or by using an order fulfillment service provider.
In terms of logistics and your online company, shipping and handling are essential. A lot goes into keeping consumers pleased while still keeping expenses low, such as providing appropriate delivery options and negotiating advantageous shipping prices.
SUMMARY
Internal warehousing vs. third-party logistics: consider internal warehousing, which gives you more control. Storage space, machinery, equipment, and trained personnel to help with various order fulfillment duties must all be bought. The more SKUs you have, the more storage fees your 3PL provider will charge you. Want to read on transportation management? Click here.
At Instructor Brandon | Dynatuners, we always seek innovative methods to improve your competitiveness and suit your Microsoft Dynamics 365 requirements. Our offerings are founded on defined procedures, industry experience, and product understanding. If you’re interested in consulting with our specialists on how it may benefit you to achieve transparency in business processes, don’t hesitate to Contact Us.
What precisely is an invoice error?
If an inaccurate invoice is sent, the company must send a cancellation invoice with a new invoice number. This will include the original invoice number and the date it was issued, as well as a negative invoice amount. Then, with a new invoice number, a valid invoice can be raised.
What does it mean to pay a processing and handling fee?
A handling fee is defined as a cost charged to a consumer to cover expenses not related to the goods or shipping. Instead, handling costs account for more aspects of the fulfilment process, such as: Costs of product storage
Is it necessary to include a handling fee?
A handling fee might assist offset expenses if orders travelling to a specific country or region take longer to pack. Merchants typically charge a handling fee to offset the expense of shipping materials (such as boxes, tape, and labels).

 1994
1994