Supply Chain and Logistics Management
Understanding Inventory Cycle Counting Process in Dynamics 365
Understanding Inventory Cycle Counting Process in Dynamics 365
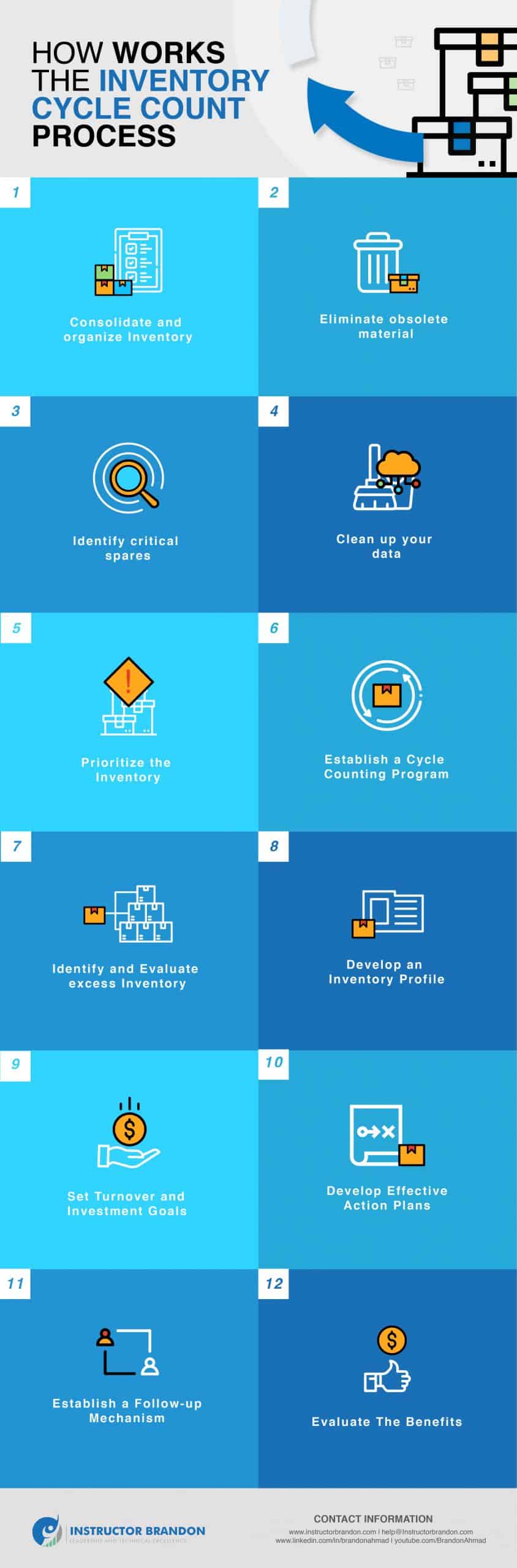
Understanding inventory cycle counting process in MS Dynamics 365 explains how to improve the accuracy and reliability of inventory control. The inventory cycle count process is a method to improve the accuracy and sureness of inventory control. This process is about counting warehouse inventory. Basically, it is putting together, following a criterion. We count the products frequently and regularly. So, we do not perform a single annual physical inventory.
Microsoft Dynamics 365 offers you the perfect tool to implement cyclical counts in your company and automate your internal processes. Companies rely on their inventory for constant cash flow and customer satisfaction. It is very important to find the most efficient inventory counting process. They are sure that the inventory is managed, stored and tracked if they are controlling the inventory volume through cycle counting; without shrinkage or loss. However, cyclic counting in inventory count include much more than simply counting the number of products or ingredients in a storage space. We are here to explain it in detail for you to decide if this method is the most convenient for your company.
What is an Inventory Cycle Count Process?
The inventory cycle count process is a very common inventory technique in small and medium sized warehouses. But what exactly does it mean? This method consists of regularly counting groups of references instead of do a single annual inventory. These reference groups are determined by a criterion that can be their turnover rate (A, B, C), size, reference type, etc.
The advantages of taking a cycle count process as opposed to an annual or half-yearly one is that the risk of stock breaks is reduced; greater knowledge of the references stored is guaranteed and, above all, the detection of errors and mismatches between the Enterprise Resource Planning ERP and the Warehouse Management System WMS with the actual warehouse is eased.
Types of Cyclical Inventories
There are three methods of cyclical inventory, according to the criteria applied when we determine the counting groups:
It is the most common technique in warehouses, based on the Pareto principle; according to which 20% of references represent the 80% of sales. Bearing this in mind, the warehouse manager must assign an A, B or C rotation to each reference according to its sales frequency (A is the highest rotation category and C the lowest). In a cycle counting inventory, we count the type A products more frequently than type C products.
This is the ideal process if you are implementing the cycle counting for the first time. The logistics managers choose a series of SKUs, which will be inventoried several times during a short period of time. The objective of this method is to locate stock-counting errors and improve the agility of the inventory process.
3. Inventory Cyclic Random Counting:
When references are of similar characteristics ─rotation, size, weight, value, etc., the cyclic random counting is applied. This means that groups are created randomly, as there is no relevant characteristic that differentiates the different SKUs.
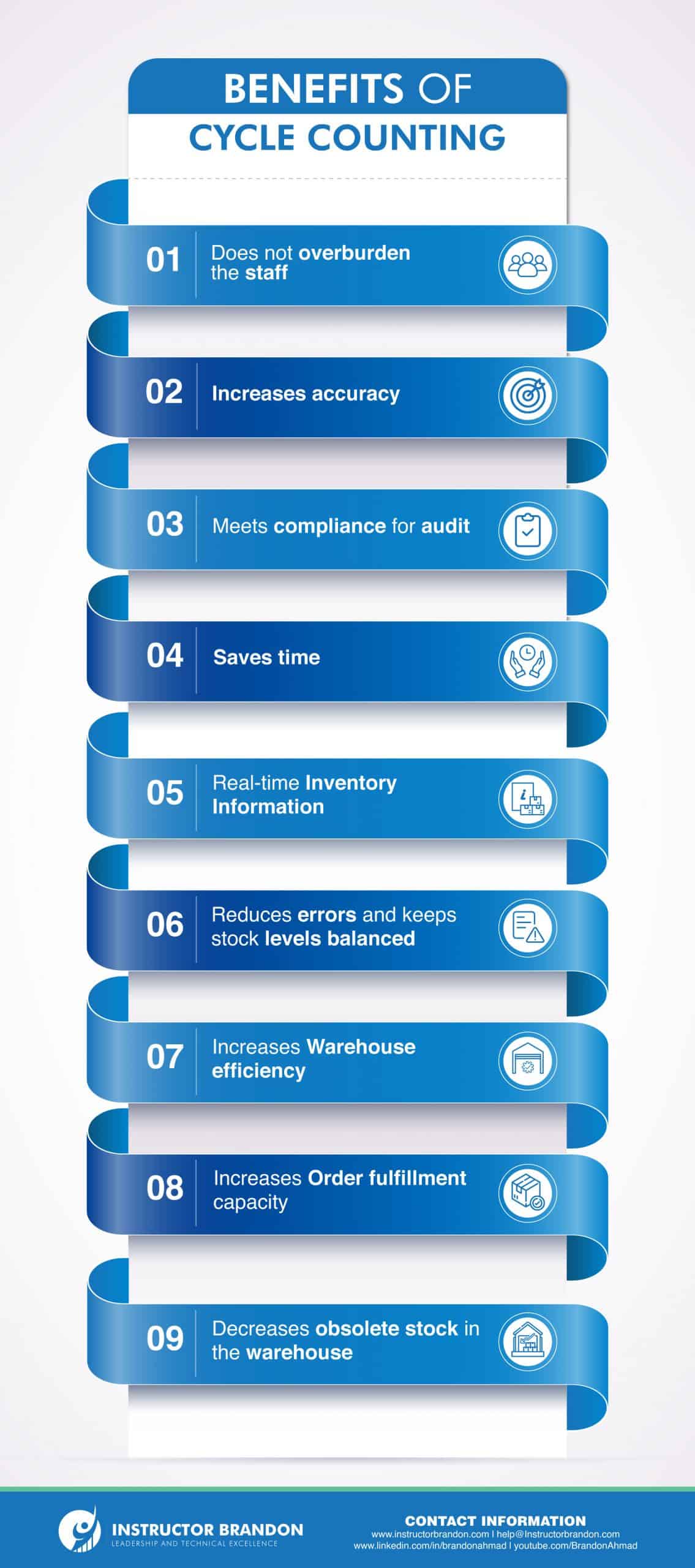
Advantages and Disadvantages of Implementing Inventory Cycle Counting
Cycle Counting of Inventory allows:
- A more accurate stock record; an easily measurable improvement by tracking the IRA Inventory Registration Accuracy indicator
- Organizing efficiently the counting of items, reducing the work of a single annual inventory
- Expediting the detection and removal of defective or damaged items
- It allows maintain the productivity when we are counting stock without interrupting other logistics operations.
- Making better logistical decisions in purchasing, in storage or in order preparation
In general, the cyclical inventory count permits a better control over the references in the warehouse; skipping difficult situations to the company as the breakage of stock or over stocking.
In this way, the cyclical count also presents some disadvantages:
- It must be properly planned (a counting strategy must be established that covers all references in a reasonable period of time)
- Requires booking a time in the daily routine of the company
- Also must be assumed that there will be references that are less controlled than others (those with lower rotation, normally)
Cyclic Counts vs. Physical Counts
When companies decide to implement systematic inventory counts, they must choose a method that serves their unique business. Some companies conduct annual physical counts, while others find that cyclical counts are best for their companies, inventory levels and labor budget.
Cycle Counts
Cycle counting is a process that saves time and money invested in inventory management by counting only the stock of selected items at a time. This type of method eliminates the need to take stock counts of the entire warehouse at once, saving companies funds on multiple workers over an extended period of time. The cycle count process also increases productivity, avoids human error and does not require warehouses to stop their operations to perform inventory checks. Cycle counting programs are common in warehouse inventory management because they are fast, easy and reliable.
By taking a sample of certain items from around the warehouse, companies can obtain an estimated figure to determine the total amount in storage. Because performing a cycle count process does not require closing the warehouse, it can also be practiced daily. The accuracy of cycle counts can be increased through the use of inventory tracking software, which alerts users when an error has happened so that it can be rectified shortly. As an example, if a warehouse chief enters the day’s cycle count data and contradicts the quantity in the system, the software will notify the user. The manager can then see if they have miscounted, misspelled, or if the action is actually lost.
Physical Counts
With a Physical inventory counting we have a little bit more of job, because we count every product one by one. This usually requires operations to stop and takes employees days to complete; depending on the size of the business. In the same way, this does not mean that external services will also stop. Besides, any simultaneous inbound or outbound shipments that we take into account when totaling stock quantity levels.
Physical inventory has a lot of human mistakes, and can result into stock discrepancies.
Stock discrepancies due to excess or under stocked goods can reduce a company’s profit margins and increase their expenses. Sadly, this event is not uncommon, as 30% of companies have by mistake sold out-of-stock items; leaving unsatisfied customers and unmanaged orders. While discrepancies and stock imprecisions are a business nightmare; implementing proper inventory cycle counts can prevent them.
How to do a Cycle Count Job with Microsoft D365?
We describe the process of cyclic counting with Dynamics 365 in three steps:
1. Create A Cyclic Counting Job:
The cyclic counting work is done naturally using the article threshold parameters or through a cyclic counting plan. You can also manually create cycle counting jobs using the warehouse or article parameters on the ‘Cycle Count Job by Article’ or ‘Cycle Count Job by Location’ pages.
2. Process the Cycle Counting:
After creating the cycle counting job, perform the cycle counting job by counting the items in a warehouse location and then using a mobile device to specify the result in Dynamics 365 Supply Chain Management. Instead, you can count the items in a warehouse location without creating the cycle counting job. The name of this process is ‘one-time cycle counting’.
3. Resolving Count Value Differences:
After a cyclic count, all items that have count-value differences will have a pending Review job status on the ‘All Job’ page. You can resolve these differences on the ‘Pending Review’ page of the cyclic count job.
Requirements before Performing the Cyclic Count in Microsoft Dynamics 365:
- Item: The item must be available for warehouse management processes
- Warehouse: The warehouse has to be able for warehouse management processes
The process for habilitate these processes in your warehouse is as follows:
- Go to the Warehouse page
- Select the store
- Then select the option ‘Use warehouse management processes’
However, to allow workers to move pallets during a cyclic count, you need to do the following:
- Select the ‘Warehouse Management drop-down tab’
- Then select the option ‘allow pallet movements during cyclic counting’
Workgroups:
This is completely optional; but Dynamics 365 allows you to create a workgroup to segregate warehouse work depending on the type of work.
Locations:
To enable cyclic counting for a warehouse location, the first thing to do is:
- Enable cyclic counting of storage bins
- Go to Location Profiles
- Select the option ‘Allow cyclic counting’
Warehouse management parameters:
With this option, you can set parameters for the cyclic counting.
- First go to the Warehouse Management Parameters page
- Specify the default setting type code, Job Class ID, and job priority for the cycle count
How to Use It on Mobile Devices:
To use this feature of Dynamics 365 to manage and monitor your inventory through a mobile device, create a menu item for one of the following methods on the Mobile Device Menu Items page:
- User-directed cyclic counting
- System-driven cyclic counting
- Grouping of cyclic counts
- Cyclical counting on time
- Set up a menu for the mobile device
- Create a work user account and assign a mobile device menu to the work user ID
- Finally, choose ‘Automatically Create Cyclic Count Job’
Recurring Creation of the Cyclic Counting Job
There are two ways to schedule the recurrent creation of the cyclic counting job: set cyclic counting thresholds or set cyclic counting plans.
- A cycle count threshold indicates the limit of quantity or percentage of inventory items. When we reach the threshold limit, the cycle counting job is automatically made.
- The cycle counting plan creates cycle counting jobs instantly or periodically through a batch job. When this is created, the cycle counting job line include information about the location to be counted.
The available inventory related with this bin is not blocked and is therefore available for the booking and checkout process, even if there is an open count job.
Create a Cycle Counting Job Based On Threshold Parameters for Articles
Cyclic count job can be created when the number of items is below a specific threshold value in a location. For example, there are 60 articles in a bin that has a cyclic count threshold of 40. During a sales order transaction, 25 articles are choose from the bin and placed in a temporary bin. Since the new article count, 35; is less than the threshold quantity, the cyclic count job is made accordingly for the bin.
Scheduled Cyclic Counting Job
You can schedule the cycle counting plans to create cycle counting jobs immediately or periodically. When you setting up cycle counting plans, you can control the workgroup for every cycle counting job; the maximum number of cycle counts that you create for items in different locations, and the number of days before a warehouse location. For example, if an item is available in three warehouse locations but the maximum number of cycle counts is set to 2, when the plan is done, we create two cycle counts for the two locations where the item is present.
As another example, it sets the number of days between cycle counts to 5.
In this case, every five day we made a new cycle count job. This means, if we process the cycle counting job on day 3, we create the next cycle counting job five days after the last cycle counting job, it means on day 8.
Creating a Cycle Count Job Manually
To create the Cyclic Count Job manually, you can use the Cyclic Count Job by Item or Cyclic Count Job by Location pages. You can specify the maximum number of cyclic counts that you want create. For example, the warehouse manager put a value of five, so the cyclic counting work is done in five places, even that the item is present in 10 places. You can also select a workgroup ID for which the cycle counting job IDs are.
Performing a Cyclic Count Using a Mobile Device
There are several methods to process a cyclic counting job using Supply Chain Management on a mobile device:
1. User-Driven:
The worker can specify a job ID for the cyclic counting job that has the status of Open.
2. System-Driven:
Supply Chain Management assigns the worker a cyclic-counting job ID.
3. Cyclic Count Job Grouping:
The worker can group the Cyclic Count Job IDs that are specific to a particular location, area, or job group.
4. One-Time Cycle Counting:
The worker can count the items in a warehouse location at any time, without creating the cycle counting job. To do spot cyclic counting in a storage bin, the worker specifies the bin ID.
8 Simple Steps to Implement a Cycle Count Process
After deciding which method of cyclic counting is the best to its situation, a company has to implement the control processes correctly.
General measures for this include the following:
- Collect all the information and useful data to identify possible inventory discrepancies
- Create small portions of inventory to manage distribution
- Create a program and assign inventory duties to employees
- Select experienced staff members for the audit process
- Delay inbound and outbound shipments when performing cyclic counts
- Keep a note of the processes used and analyze the records to identify errors and inventory discrepancies
- Generate detailed reports of all inventories at their respective locations for future reference and analysis
- Perform routine inspections of warehouses and storage locations to ensure proper maintenance
Conclusion: Understanding Inventory Cycle Counting Process in Dynamics 365
In conclusion, Microsoft does not stop innovating in the field of technology and at Instructor Brandon, we know this very well. We want to help you boost your career and your company’s status, so we invite you to learn about all the courses and certifications they offer; for you can become an expert and apply all these incredulous technologies in your own field of knowledge.
If you have any questions about the certifications or about how to use Microsoft Dynamics 365, please do not hesitate to contact us.

 6607
6607